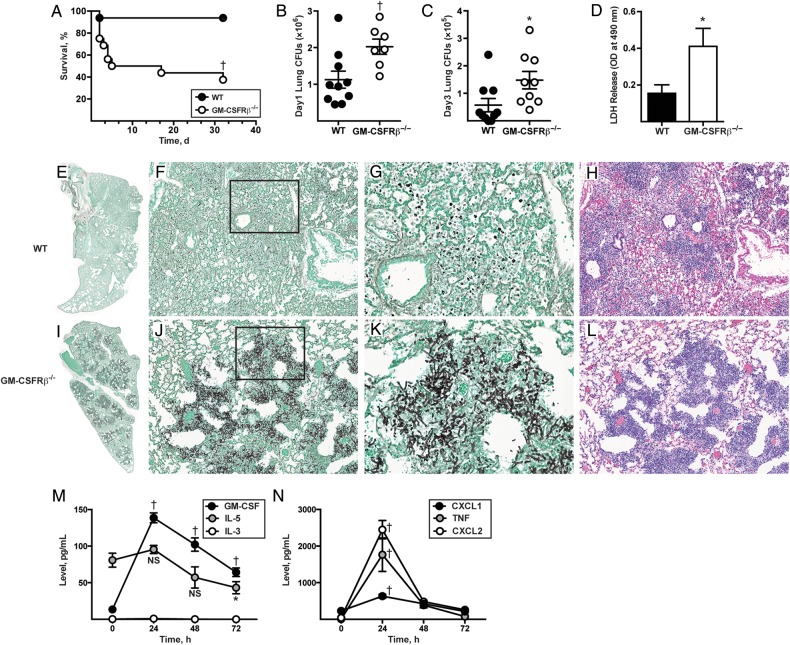
Figure 1.
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) receptor β chain (GM-CSFRβ) signaling is critical for survival, fungal clearance, and lung integrity during Aspergillus fumigatus challenge. A–D, Wild-type (WT) and GM-CSFRβ−/− mice were challenged with 8 × 107 CEA10 conidia and monitored for survival (Kaplan–Meier survival plot of WT [black circles; n = 16] and GM-CSFRβ−/− [white circles; n = 16] mice; data pooled from 2 independent experiments) (A); challenged with 3 × 107 CEA10 conidia tested for lung fungal burden 24 (B) hours and 72 (C) hours after infection (representative data from 3 experiments [B]) and 1 experiment [C]); and challenged with 8 × 107 CEA10 conidia and examined for bronchoalveolar lavage fluid lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels 48 hours after infection (bar graphs show mean [standard error of the mean {SEM}] from an experiment with 6–10 mice per genotype) (D). E–L, Representative micrographs of hematoxylin-eosin– and Gomori ammoniacal silver–stained lung sections from WT and GM-CSFRβ−/− mice 48 hours after infection. Images were captured at ×2 (E, I), ×20 (F, H, J, L), and ×60 (G, K) magnification, with G and K corresponding to insets in F and J, respectively. M, N, Graph shows mean (SEM) lung cytokine and chemokine levels at the indicated time points in C57BL/6 WT mice infected with 3 × 107 CEA10 conidia, with representative data from 1 of 2 independent experiments (5, 8, 9 and 8 mice at 0, +24, +48, and +72 hours, respectively). *P < .05; †P < .01. Abbreviations: CFUs, colony-forming units; IL-3, interleukin 3; IL-5, interleukin 5; NS, not significant; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.