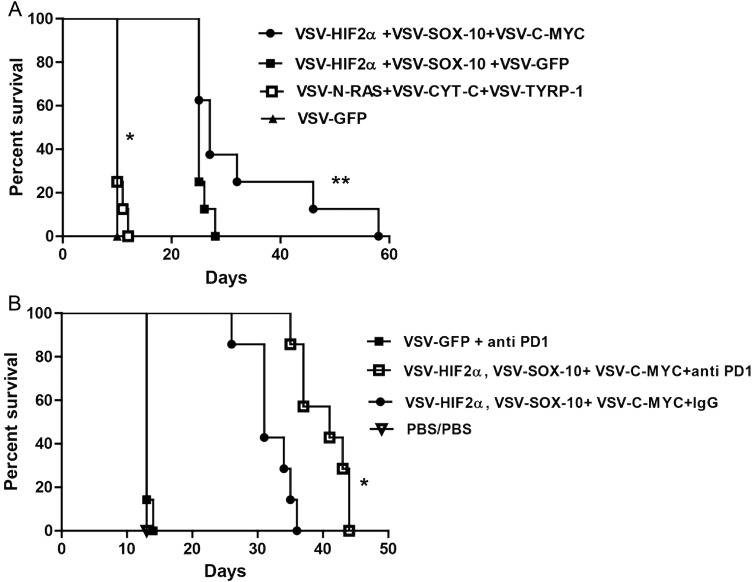
Fig. 4.
VSV-TAA therapy of intracranial GL261 tumors with checkpoint inhibition. (A) C57BL/6 mice bearing 5-day established i.c. GL261 tumors were treated intravenously (n = 7–8 mice per group) with a total of 5 × 106 plaque-forming units (pfu) of VSV-HIF-2α, VSV-Sox-10, and VSV-c-Myc; VSV-HIF-2α, VSV-Sox-10, and VSV-GFP; VSV-N-Ras, VSV-Cyt-c, and VSV-TYRP-1; or VSV-GFP on days 6, 8, and 10; 13, 15, and 17; 20, 22, and 24; and 27, 29, and 31, respectively. Survival with time is shown. Representative of 3 separate experiments. *P = .0001 between VSV-HIF-2α, VSV-Sox-10, and VSV-c-Myc and VSV-GFP, and **P = .0414 between VSV-HIF-2α, VSV-Sox-10, VSV-c-Myc and VSV-HIF-2α, VSV-Sox-10+, VSV-GFP. (B) C57BL/6 mice bearing 5-day established i.c. GL261 tumors were treated intravenously (n = 7–8 mice per group) with a total of 5 × 106 pfu of VSV-GFP; VSV-HIF-2α, VSV-Sox-10, and VSV-c-Myc, or PBS on days 6, 8, and 10; 13, 15, and 17; and 20, 22, and 24, respectively. On days 13, 15, and 17 and 20, 22, and 24 these groups were treated intravenously with either PBS, control IgG antibody, or anti-PD1 antibody at 10 mg/kg/mouse as shown. Survival with time is shown. Representative of 2 separate experiments. *P = .0006 between VSV + anti-PD1 combination and VSV combination alone.