Figure 5. Arrhythmia triggers in patch‐clamped ventricular myocytes .
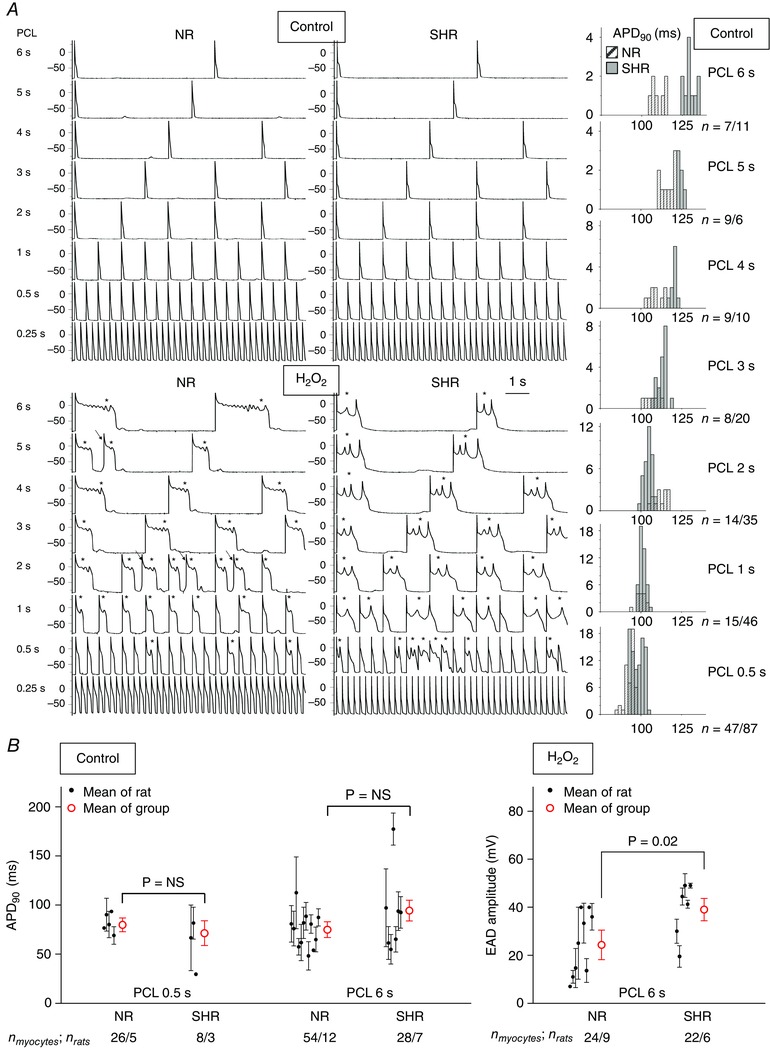
A, although even 2 mmol l−1 H2O2 cannot induce VT/VF in NR intact hearts, 0.15 mmol l−1 H2O2 induces VT/VF arrhythmia triggers, such as EADs (*) and triggered activity (arrows) in this representative NR myocyte just as readily as in the representative SHR myocyte. Compared to the NR myocyte, the SHR myocyte has slightly more prolonged APs during slow pacing (PCL ≥3 s) at baseline (upper panels and histograms) and EADs with lower frequencies and larger amplitudes during H2O2 exposure (bottom). n, number of APs from the representative NR/or SHR myocyte. B, compared to NR myocytes, SHR myocytes do not have excessively prolonged APD90 during either PCL at stress‐free baseline but have slightly larger stress‐induced EAD amplitudes during of PCL 6 s. The mean ± SEM for each rat is represented by a small black circle with whiskers, for each group by a large red circle with whiskers. n myocytes/n rats, number of myocytes/number of rats.
