Figure 1. Location and phenotype of RTN neurons .
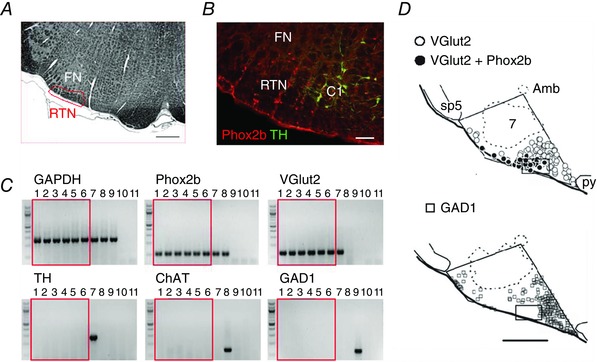
A, transverse section through the caudal end of the facial motor nucleus (FN, Sprague–Dawley adult rat; bregma −11.6 mm; myelin stain; scale 500 μm). Box showing approximate location of retrotrapezoid nucleus. B, RTN identified as Phox2b‐immunoreactive (Phox2b‐ir), non‐catecholaminergic (TH‐negative) neurons in a transverse section of medulla oblongata (bregma −11.6 mm; adult Sprague–Dawley rat; scale bar: 100 μm). The C1 (adrenergic/glutamatergic) neurons also express Phox2b (reproduced from Guyenet, 2008). C, single‐cell RT‐PCR data showing presence of Phox2b and VGlut2 transcripts in enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP)‐expressing neurons dissociated from the RTN of a Phox2b‐eGFP mouse (lanes 1–6), including three pH‐sensitive neurons examined after recording (lanes 4–6); the RTN neurons did not express tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), choline acetyl‐transferase (ChAT), or glutamate decarboxylase 1 (GAD1). Control experiments verified detection of the following: TH (with Phox2b and VGlut2) in a C1 neuron (lane 7); ChAT (and Phox2b) in a facial motoneuron (lane 8); and GAD1 in a striatal medium spiny cell (lane 9). Glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) expression was seen in all cells, and negative controls for each PCR reaction included bath solution (lane 10) and water (lane 11) substituted for cell contents (reproduced from Wang et al. 2013 b). D, plots of glutamatergic (VGlut2‐mRNA+) and GABAergic (GAD1‐mRNA+) neurons in a representative transverse section through the rat's medulla oblongata (bregma level −11.4 mm; calibration 500 μm). Box shows predominance of glutamatergic neurons in RTN. All Phox2b‐ir neurons express VGlut2 (filled circles); none contain GAD1. The Phox2b+ neurons, most of which are non‐catecholaminergic at this coronal level, are closely surrounded by Phox2b‐negative glutamatergic neurons and Phox2b‐negative GABAergic neurons (reproduced from Stornetta et al. 2006). Amb, nucleus ambiguus, compact part; sp5, spinal trigeminal tract; 7, facial motor nucleus; py, pyramidal tract.
