Figure 2. Inputs and outputs of RTN neurons .
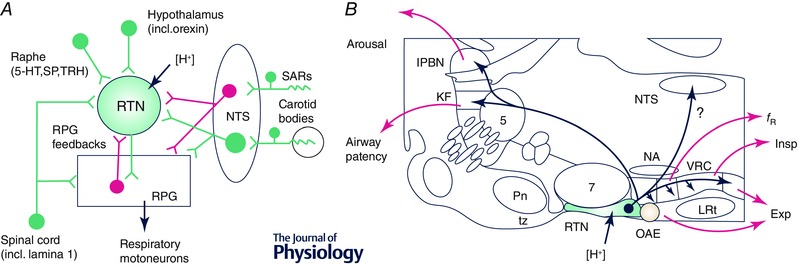
A, main connections of RTN neurons (green, excitatory; magenta inhibitory). The RPG includes the ventral respiratory column (VRC) and the dorsolateral pons. The monosynaptic nature of the RTN inputs shown in this figure has not yet been confirmed by ultrastructural evidence. B, parasagittal section through the rat's brain (∼1.8 mm lateral to the midline) illustrating the location of RTN neurons, their axonal projections and the putative function of each projection. Abbreviations: 5‐HT, serotonin; Exp, active (abdominal) expiration; f R, breathing frequency; Insp, inspiration; KF, Kölliker–Fuse nucleus; lPBN, lateral parabrachial nuclei; LRt, lateral reticular nucleus; NA, nucleus ambiguus; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; OAE, oscillator for active expiration; Pn, pontine nuclei; RPG, respiratory pattern generator; SARs, stretch‐activated receptors; SP, substance P; TRH, thyrotropin‐releasing hormone; tz, trapezoid body; VRC, ventral respiratory column (incl. its four subdivisions, from rostral to caudal: Bötzinger, preBötzinger complex, rVRG and cVRG).
