Figure 1. Acute hypercapnia attenuates forskolin‐stimulated cAMP levels in Calu‐3 cells independent of changes in intracellular pH .
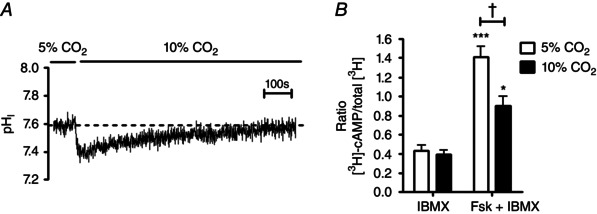
A, the effect of hypercapnia (10% CO2) on the pHi of Calu‐3 cells; cells recovered pHi from CO2‐induced acidosis after ∼20 min. B, the effect of acute hypercapnia on intracellular cAMP in which cells were incubated for 20 min in either 5% CO2 (v/v) in air or 10% CO2 (v/v) in air before being stimulated with either IBMX (1 mm) or forskolin (5 μm) + IBMX (1 mm) for a further 10 min. Intracellular cAMP levels were determined by measuring the amount of [3H]‐cAMP in each sample. ***Significant effect of forskolin (P < 0.001; *P < 0.05); †significant effect of hypercapnia (P < 0.05). Data represent mean ± SEM; n = 6 for each.
