Figure 5.
Studies on Zebrafish Embryos
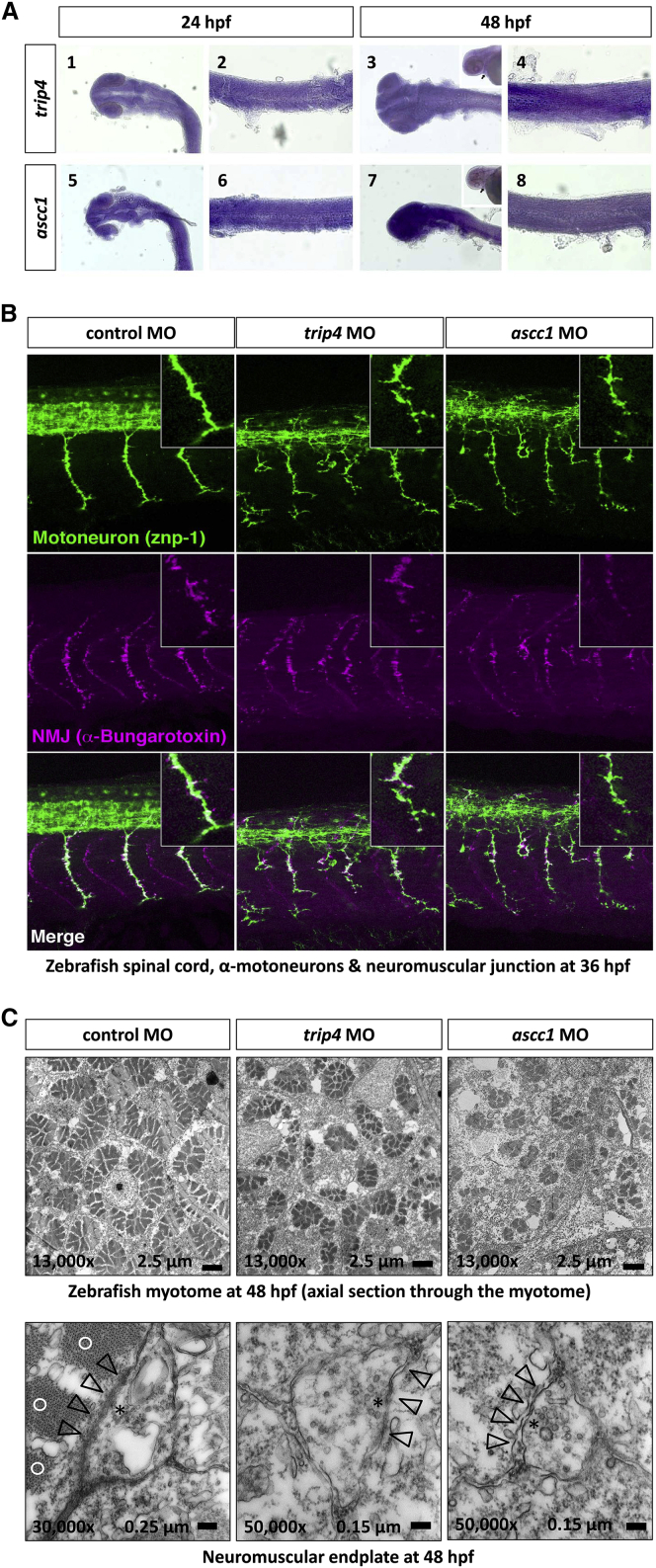
Expression of trip4 and ascc1 mRNA.
(A) trip4 is expressed ubiquitously in the head (A1) and trunk (A2) at 24 hpf and at 48 hpf (A3 and A4). ascc1 is also expressed ubiquitously in the head (A5) and trunk (A6) at 24 hpf and 48 hpf (A7 and A8). The arrowheads indicate the heart, verifying that both trip4 and ascc1 are expressed in cardiac muscles.
(B) MO-mediated trip4 and ascc1 knockdown in zebrafish larvae led to a severe derangement of α-motoneuron axons and the myotome. In the morphants, we found a perturbed outgrowth of α-motoneuron axons projecting to the trunk muscle in every somite segment at 36 hpf. The α-motoneurons were short, thin, and fragile with abnormal branches in trip4 morphants and ascc1 morphants. In these morphants, we additionally see ectopic outgrowth of motoneurons from the spinal cord. The α-motoneurons are labeled with the znp-1 antibody (green). Labeling with α-bungarotoxin (purple) displays the formation of neuromuscular junctions that form along with the α-motoneurons. The neuromuscular junctions were thin, reduced in number, and disorganized in the trip4 and ascc1 morphants.
(C) Electron-microscopic images of axial sections through the zebrafish myotome at 48 hpf. The rosette-like formation of myofibrils is greatly disturbed with reduced size and numbers. The lower panels show a neuromuscular endplate of the control morphants (left) with a normal thickened basal lamina, which is directly adjacent to the contractile elements of the myofibril. This is in contrast to the endplates from the trip4 and ascc1 morphants, which are smaller and have a disrupted basal lamina and no adjacent contractile elements. An asterisk denotes clusters of neurotransmitter vesicles (vesicle diameter 30–40 nm); open arrowheads denote the synaptic cleft and basal lamina of the neuromuscular endplate; open circles denote sarcomers (contractile elements) in the vicinity of the neuromuscular endplate. Note the higher magnification of the morphant endplate.