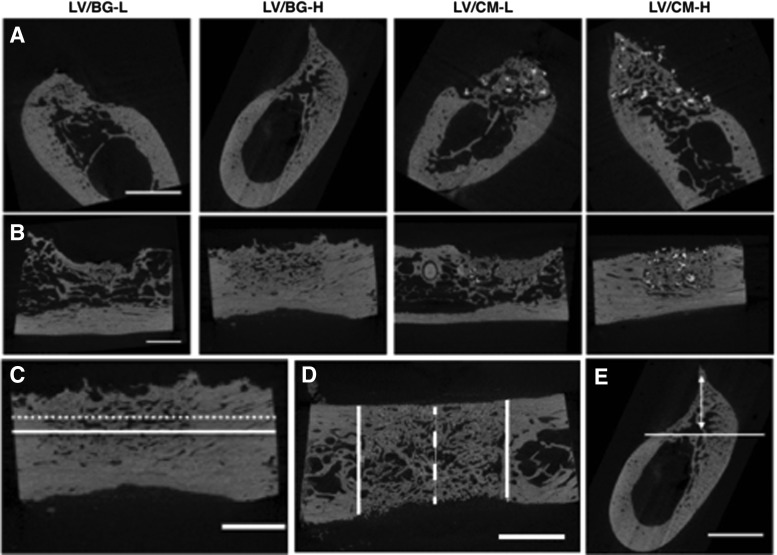
FIG. 3.
Micro-computed tomography (μCT) analysis. (A) Representative 2D images of axial (coronal plane) cross sections. (B) Representative 2D images of longitudinal (sagittal plane) cross sections. (C) Schematic illustrating measurement of ridge width from a 2D longitudinal cross section at 2 mm (solid line) and 4 mm (dotted line) above the base of the defect. (D) Schematic illustrating measurement of ridge width from a 2D transverse plane cross section. Normalized ridge width was calculated as the width measured at the mesiodistal center of the defect (dashed white line) divided by the average width of the host bone bone (solid white lines). Measurements were taken at heights 2, 4, and 6 mm above the base of the defect (shown in C). (E) Representative image depicting measurement of the maximum ridge height in 2D longitudinal sections at the mesiodistal center of the defect. The solid line shows the base of the defect, and the double arrow represents the maximum ridge height. The scale bar denotes 5 mm.