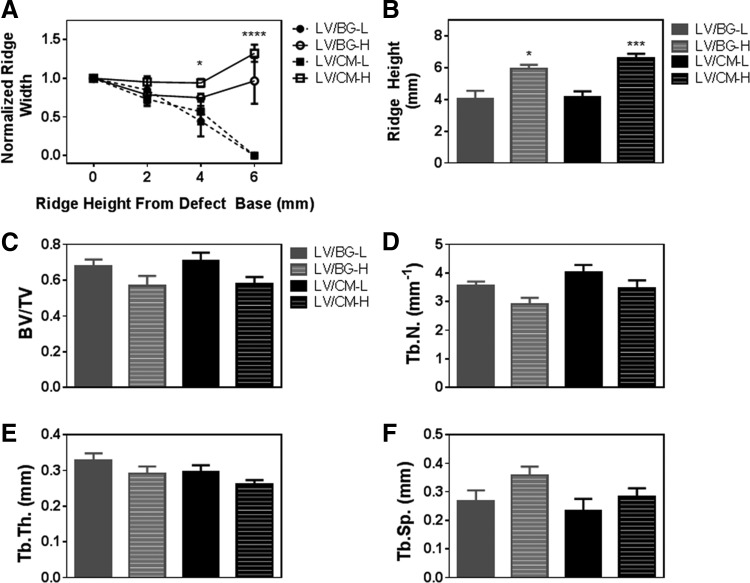
FIG. 4.
Quantitative analysis of space maintenance and new bone formation by μCT. (A) Normalized ridge width measured at the mesiodistal center of the defect as a function of height above the baseline of the defect. Ridge width measured for the LV/CM-H group was significantly greater than that measured for the LV/BG-L at 4 mm above the base of the defect (p < 0.05). Both high-dose treatment groups showed significantly higher ridge heights compared to the low-dose groups at 6 mm above the base of the defect (p < 0.0001). (B) Maximum ridge height measured at the mesiodistal center of the defect. Significant differences between low- and high-dose groups are denoted by *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001. No significant differences between LV/BG-L and LV/CM-L or between LV/CM-L and LV/CM-H were observed. (C–F) Morphometric parameters measured from μCT images: (C) bone volume/total volume (BV/TV), (D) trabecular number (Tb.N.), (E) trabecular thickness (Tb.Th.), and (F) trabecular separation (Tb.Sp.) No significant differences in morphometric parameters were observed between groups.