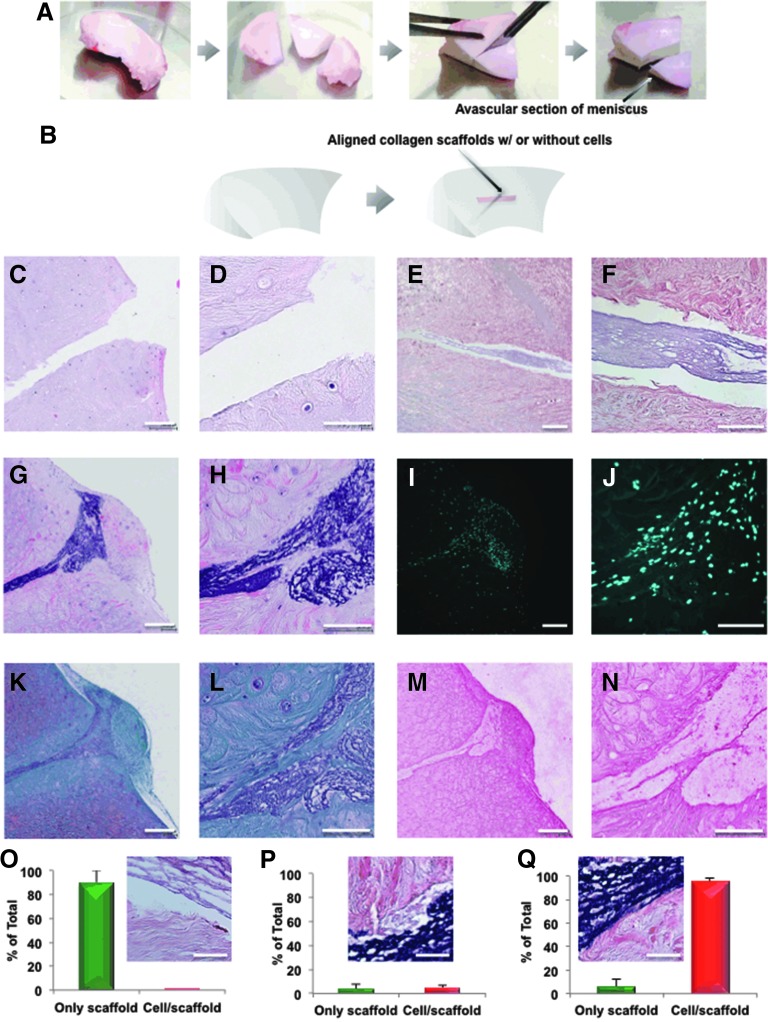
FIG. 4.
Overview of the bovine meniscus ex vivo repair model: creation, histology, and histomorphometric analysis. (A) Fabrication of avascular section of meniscus. (B) Coronal defects were surgically produced in bovine meniscus white zone tissue and 4-week-old meniscus avascular cell-seeded aligned collagen scaffolds were inserted and cultured for a further 3 weeks. Nontreated defects and non-cell seeded collagen scaffolds were used as controls. The scaffold was placed within the coronal defect of bovine meniscal avascular zone. All constructs were cultured for 3 weeks and then processed for histology. (C, D) H&E stain of only defect in meniscus. (E, F) H&E stain of only collagen implant. (G, H) H&E stain of the cells/aligned collagen scaffold implant within the defect of meniscus. (I, J) DAPI stain of the cells/aligned collagen scaffold implant. (K, L) Safranin O/fast-green stain of the cells/aligned collagen scaffold implant. (M, N) Collagen type I immunostaining of the cells/aligned collagen scaffold implant. [Mag. (C, E, G, I, K), and (M) = 10×, scale bar: 200 μm; Mag. (D, F, H, J, L), and (N) = 40×, scale bar: 100 μm]. Histomorphometric analysis of meniscus integration in the above histological sections: (O) the % disintegration (p < 0.0001), (P) the% apposition (no significant difference), and (Q) the % integration (p < 0.0001) (scale bar: 50 μm). The % of disintegration, apposition, or integration divided into each morphological group was calculated according to Pabbruwe's study.38,39 DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea