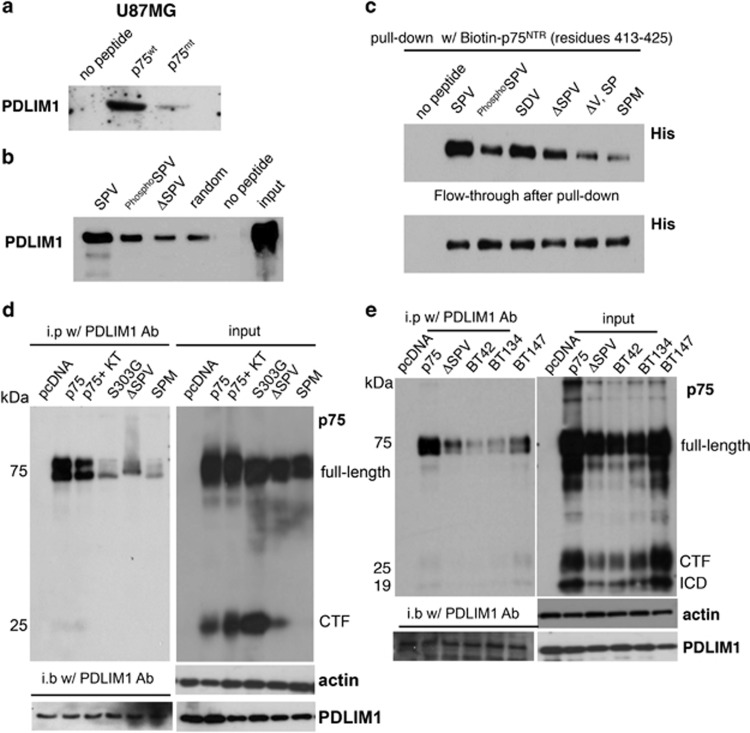
Figure 5.
PDLIM1 associates with p75NTR via the C-terminal PDZ-binding motif, an interaction regulated by phosphorylation of S425. (a) Using a biotinylated peptide to the C-terminus of either p75NTR (p75wt peptide, Biotin-N-LCSESTATSPV-COOH, residues 417-427) or a Valine deletion mutant of p75NTR (p75MT peptide, biotin-N- LCSESTATSP-COOH, residues 417-426) as affinity reagents, PDLIM1 was confirmed as a p75NTR-interacting protein by western blot analysis. (b) To assess the physiological relevance of the phosphorylation of S425 within the PDZ-binding motif, biotin-labeled peptides corresponding to the p75NTR wild-type C-terminal (SPV), the S425 phosphorylated C-terminal (PhosphoSPV) and the PDZ-binding motif deleted C-terminal (ΔSPV) were used as affinity reagents. PDLIM1 was shown to interact with maximum affinity to the wild-type unphosphorylated peptide. (c) Biotin-labeled p75NTR peptides (SPV, PhosphoSPV, ΔSPV, ΔV, SP and SPM) were incubated with His-tagged recombinant PDLIM1 protein, respectively. Pull-down assays were performed to determine the amount of PDLIM1 protein bound to each peptide. Flow-through shows unbound proteins after incubation. (d) Immunoprecipitation with PDLIM1 antibodies co-precipitated p75NTR and PDLIM1 while the mutant alleles of p75NTR (S303G, ΔSPV and SPM) or p75NTR cells treated with the PKA inhibitor KT5720 (KT; 200 nM) were severely compromised for PDLIM1 binding. (e) Interaction of PDLIM1 with p75NTR was confirmed in patient-derived glioma stem cells/tumor-initiating cells (BT42, BT134, BT147) by immunoprecipitation using anti-PDLIM1. Input cell lysates were assessed by western blot analysis for expression of p75NTR and PDLIM1.