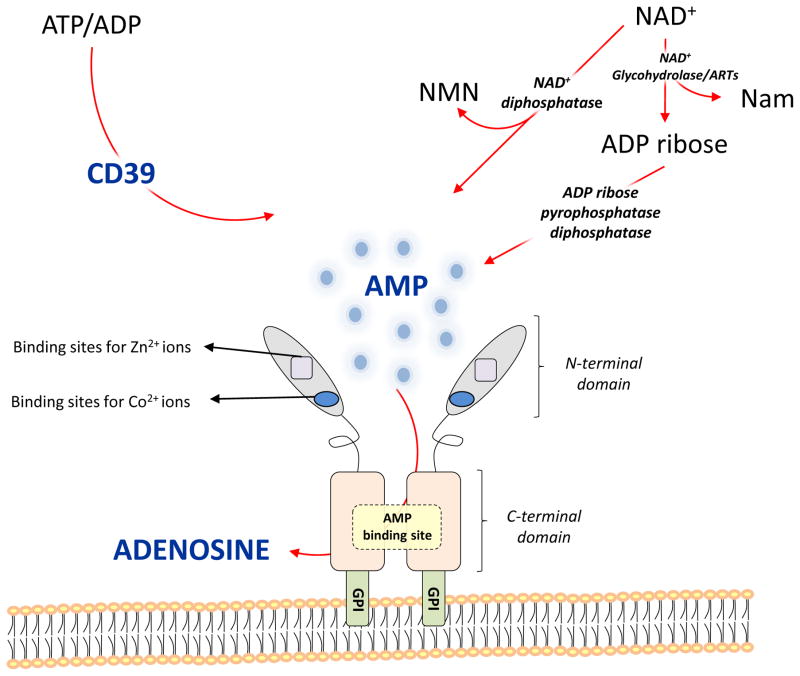
Figure 1.
Structure and role of CD73 in the extracellular metabolic pathways.
CD73 is characterized by an N-terminal domain containing binding sites for zinc and cobalt ions and a C-terminal domain containing the AMP binding site. The C-terminal domain is linked to the plasma membrane through a GPI anchor. These two domains are connected by a short α helix. Once released in the extracellular milieu, ATP and ADP are converted into AMP via ecto enzyme CD39 and further into adenosine through CD73. Extracellular NAD+ is converted into ADPribose and nicotinamide (Nam) by NAD+-glycohydrolases and ADP ribosyl-transferases (ARTs). ADP ribose can be further split to form AMP by ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase, subsequently converted to adenosine by CD73. In addition, NAD+ can also be degradated by NAD+ diphosphatase to produce nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and AMP.