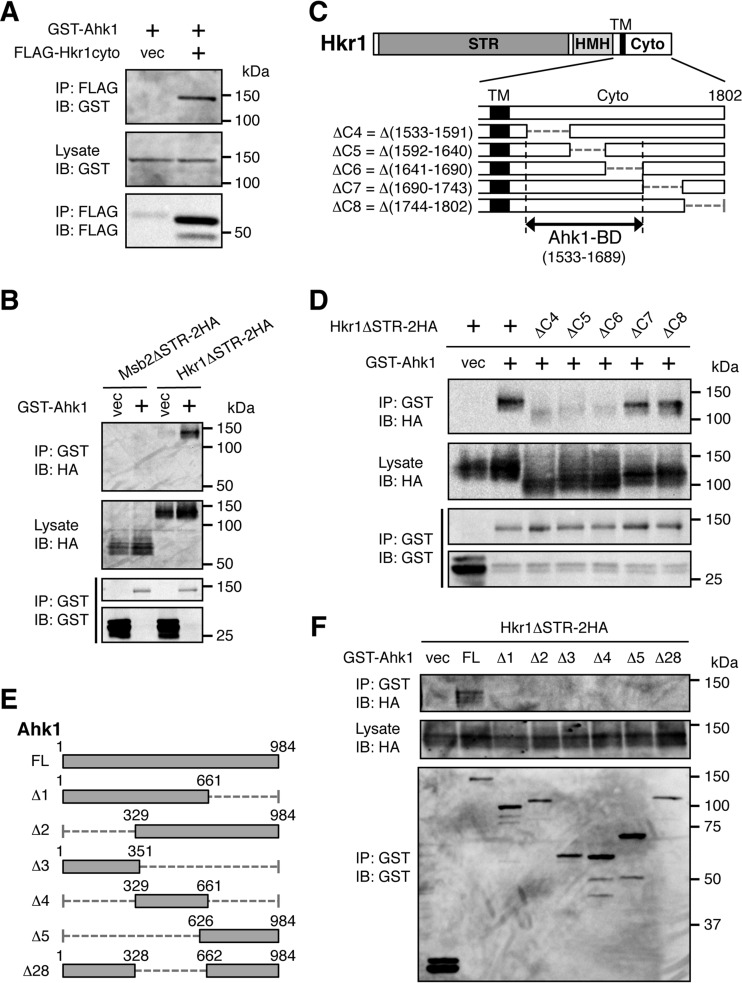
FIG 3.
Ahk1 binds to the cytoplasmic domain of Hkr1. (A) In vivo assay of the coimmunoprecipitation (coIP) of Ahk1 and the Hkr1 cytoplasmic region. The yeast strain TM257 (WT) was cotransformed with expression plasmids for GST-Ahk1 and FLAG-Hkr1-cyto (or the empty FLAG vector [vec]), both under the control of the GAL1 promoter. Transformed cells were grown in CARaf, and expression of the tagged proteins was induced by 2% galactose for 2 h. Cell extracts were prepared using buffer A. Tagged proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) from cell extracts, and coprecipitated proteins were detected by immunoblotting (IB) using the indicated antibodies. (B) In vivo assay of the coIP of Ahk1 and the membrane-associated Hkr1 molecule. TM257 was cotransformed with expression plasmids for GST-Ahk1 (or the empty GST vector [vec]) and HA-tagged Hkr1ΔSTR (Hkr1ΔSTR-2HA) or Msb2ΔSTR-2HA, all under the control of the GAL1 promoter. Cell growth, IP, and IB were conducted as described for panel A, using the indicated antibodies. (C) Schematic models of the Hkr1 cytoplasmic deletion constructs used in the experiments shown in panel D. The top bar shows the full-length Hkr1 molecule. The lower bars show enlarged cytoplasmic regions. STR, Ser/Thr-rich domain; HMH, Hkr1-Msb2 homology domain; TM, transmembrane domain; Cyto, cytoplasmic region; BD, binding domain. Numbers indicate amino acids. (D) In vivo assay of the coIP of Ahk1 and the membrane-associated Hkr1 molecule. CoIP assays were conducted as described for panel B using the deletion derivatives of Hkr1ΔSTR-2HA depicted in panel C. (E) Schematic models of the Ahk1 constructs used in the experiments shown in panel F. FL, full length. (F) In vivo assay of the coIP of Ahk1 deletion constructs and the membrane-associated Hkr1 molecule. CoIP assays were conducted as described for panel B, using the deletion derivatives of Ahk1 depicted in panel E.