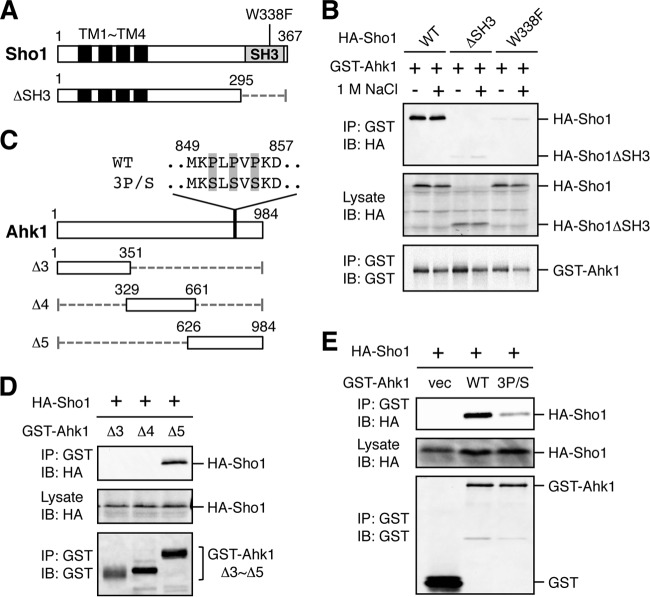
FIG 5.
Binding of Ahk1 to the SH3 domain of Sho1. (A) Schematic models of the Sho1 mutant constructs used in the experiments in this figure. TM, transmembrane domain; SH3, Src homology 3 domain. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. The dotted horizontal line represents a deleted segment. (B) In vivo assay of the coIP of Ahk1 and Sho1. TM257 was cotransformed with expression plasmids for GST-Ahk1 and HA-tagged Sho1 (HA-Sho1) or its mutant derivatives shown in panel A, all under the control of the GAL1 promoter. Transformed cells were grown in CARaf, and expression of GST-Ahk1 and HA-Sho1 was induced by 2% galactose for 2 h. The cells were further incubated with (+) or without (−) 1 M NaCl (final concentration) for 10 min. Cell extracts were prepared using buffer A. Tagged proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) from cell extracts, and coprecipitated proteins were detected by immunoblotting (IB) using the indicated antibodies. (C) Schematic models of the Ahk1 deletion constructs used in the experiments shown in this figure. The amino acid sequences of the Sho1 binding site (WT) and its 3P/S mutant are shown above the full-length Ahk1 molecule. WT, wild type; 3P/S, the P851S P853S P855S triple mutation. (D and E) In vivo assays of the coIP of Ahk1 and Sho1 were conducted as described for panel B using the Ahk1 mutant constructs depicted in panel C. NaCl was not added. vec, vector.