FIG 6.
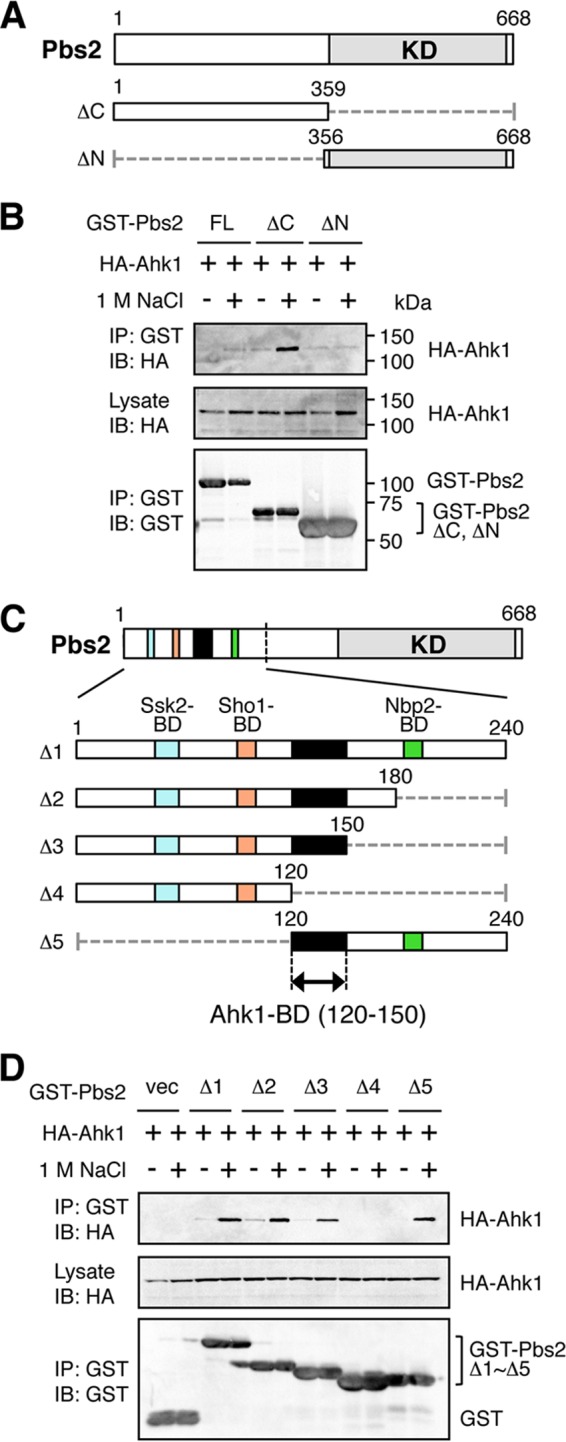
Binding of Ahk1 to Pbs2 is induced by osmostress. (A) Schematic models of the Pbs2 deletion constructs used in the experiments shown in panel B. KD, kinase domain. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. The dotted horizontal lines represent deleted segments. (B) In vivo assay of the coIP of Ahk1 and Pbs2. TM257 was cotransformed with expression plasmids for HA-Ahk1 and GST-tagged Pbs2 (GST-Pbs2) or its mutant derivatives shown in panel A, all under the control of the GAL1 promoter. Transformed cells were grown in CARaf, and expression of HA-Ahk1 and GST-Pbs2 was induced by 2% galactose for 2 h. The cells were further incubated with (+) or without (−) 1 M NaCl (final concentration) for 5 min. FL, full-length. (C) Schematic models of the Pbs2 deletion constructs used in the experiment shown in panel D. The top bar shows the full-length Pbs2 molecule. The lower bars are enlarged versions of the N-terminal noncatalytic region. Positions of previously identified binding domains (BD) are indicated by different colors. The kinase domain (KD) is indicated in gray. Black shading indicates the Ahk1-BD. (D) In vivo assay of the coIP of Ahk1 and Pbs2. TM257 was cotransformed with expression plasmids for HA-Ahk1 and the mutant derivatives of GST-Pbs2 shown in panel C, all under the control of the GAL1 promoter. CoIP assays were conducted as described for panel B. vec, GST vector.
