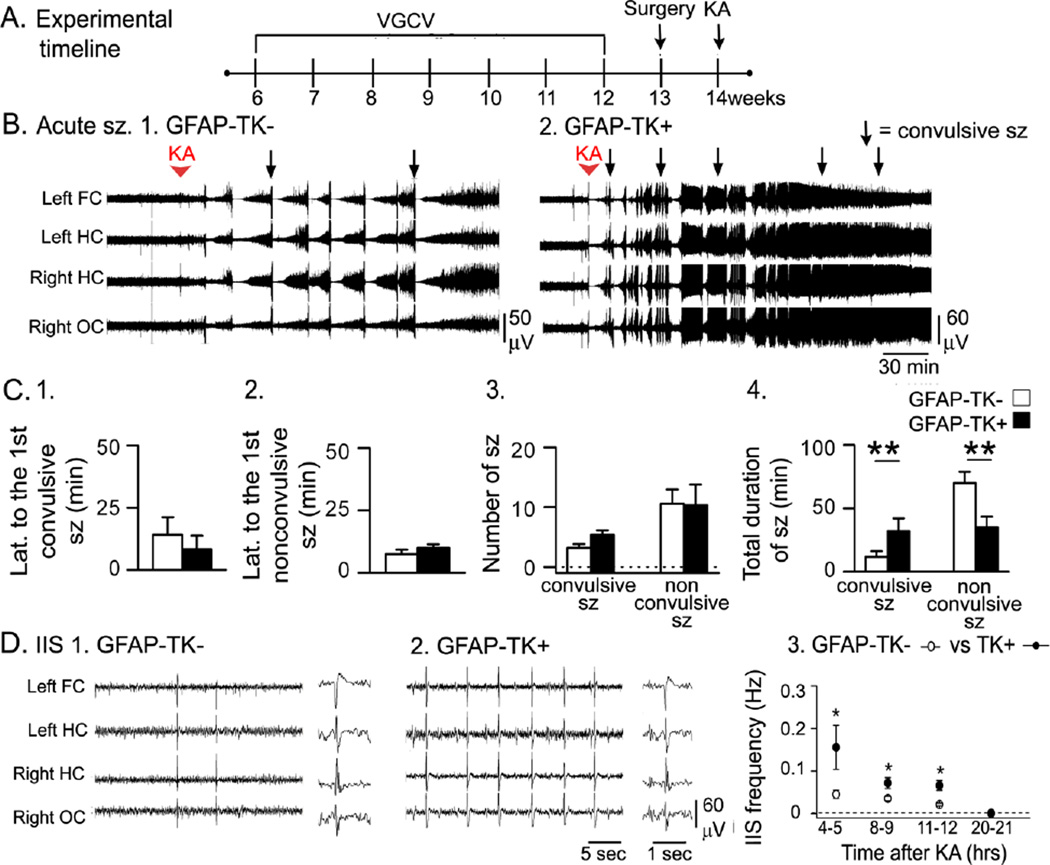
Figure 5. In mice that were not pretreated with ethosuximide, GFAP-TK+ mice had a greater response to KA than GFAP-TK− mice.
A. The experimental timeline is shown for treatment of GFAP-TK mice with 16 mg/kg KA (GFAP-TK−, n = 13; GFAP-TK+, n = 14).
B. Representative examples of the response to KA in a GFAP-TK− and GFAP-TK+ mouse show a greater response in the GFAP-TK+ mouse.
C. 1–2. GFAP-TK+ mice had similar latencies to GFAP-TK+ mice for the first convulsive and first nonconvulsive seizure. 3. There were more convulsive seizures in GFAP-TK+ mice compared to GFAP-TK− mice. 4. The total duration of convulsive seizures was greater and total duration of nonconvulsive seizures was shorter in GFAP-TK+ mice compared to GFAP-TK− mice.
D. 1–2. Representative IIS in a GFAP-TK− and GFAP-TK+ mouse.
3. GFAP-TK+ mice had a higher IIS frequency than GFAP-TK− mice.