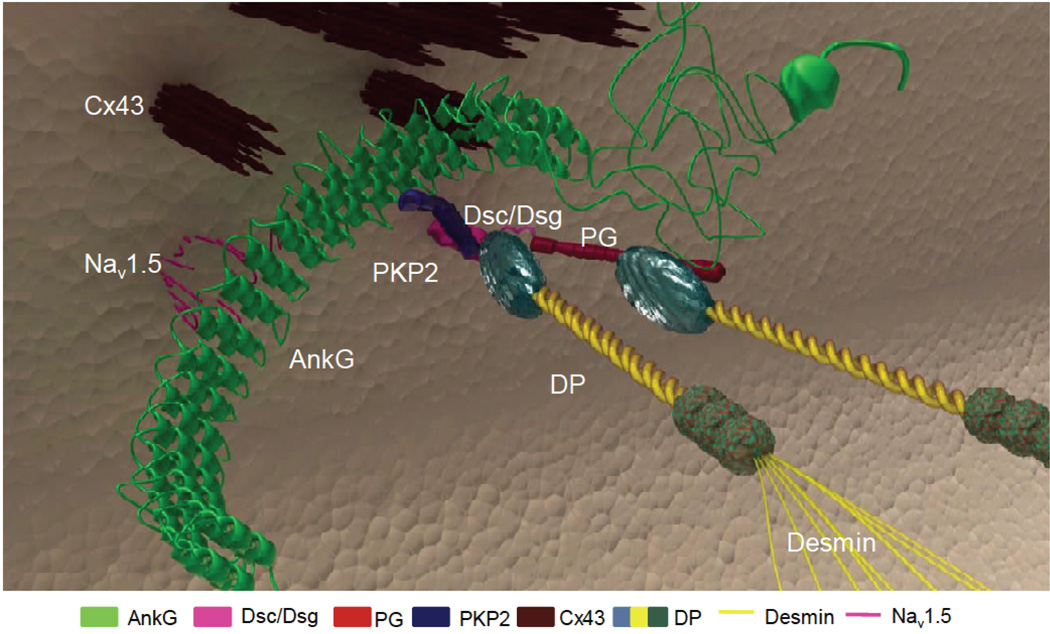
Figure 4.
Diagramatic representation of the relationship between desmosomes, gap junctions, and sodium channels at the intercalated discs. The “connexome” is a protein-interacting network where these molecules work together to coordinate excitability, cell coupling, and cell adhesion in the heart. Loss of expression of desmosomal proteins may induce electrical ventricular instability by a concomitant sodium channel dysfunction with current reduction, as a consequence of the cross-talk between these molecules at the intercalated discs. Adapted from Sato et al16.