FIG 10.
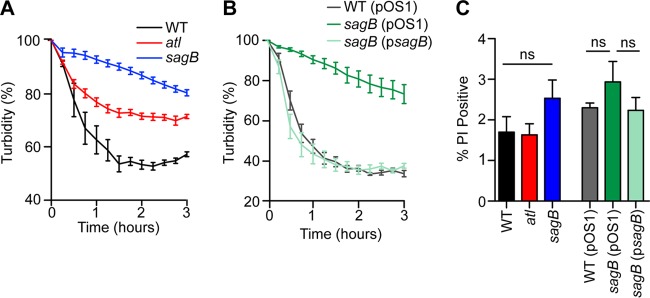
Autolysis and membrane permeability in S. aureus glucosaminidase mutants. Triton X-100 (0.05%) or buffer alone was added to mid-exponential-phase cultures (A600 of 0.5) of S. aureus suspended in 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.5). Turbidity at A600 was monitored over 3 h and plotted as the A600 of lysostaphin-inoculated staphylococci of buffer alone at each time point. Autolysis, as determined by reduction of turbidity, was compared between the wild-type, atl, and sagB strains (A). (B) Autolysis in 0.05% Triton X-100 was assessed in the wild-type (pOS1), sagB(pOS1), and sagB(psagB) strains. (C) Propidium iodide staining of bacteria was used to assess membrane permeability. One milliliter of culture (A600 of 0.5) was fixed with paraformaldehyde and subsequently stained with SYTO 9 for total cells and with propidium iodide to assess membrane integrity. SYTO 9-positive cells were analyzed for propidium iodide positivity using flow cytometry. Data from triplicate samples of 10,000 cells are presented. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. ns, not significant.