FIG 9.
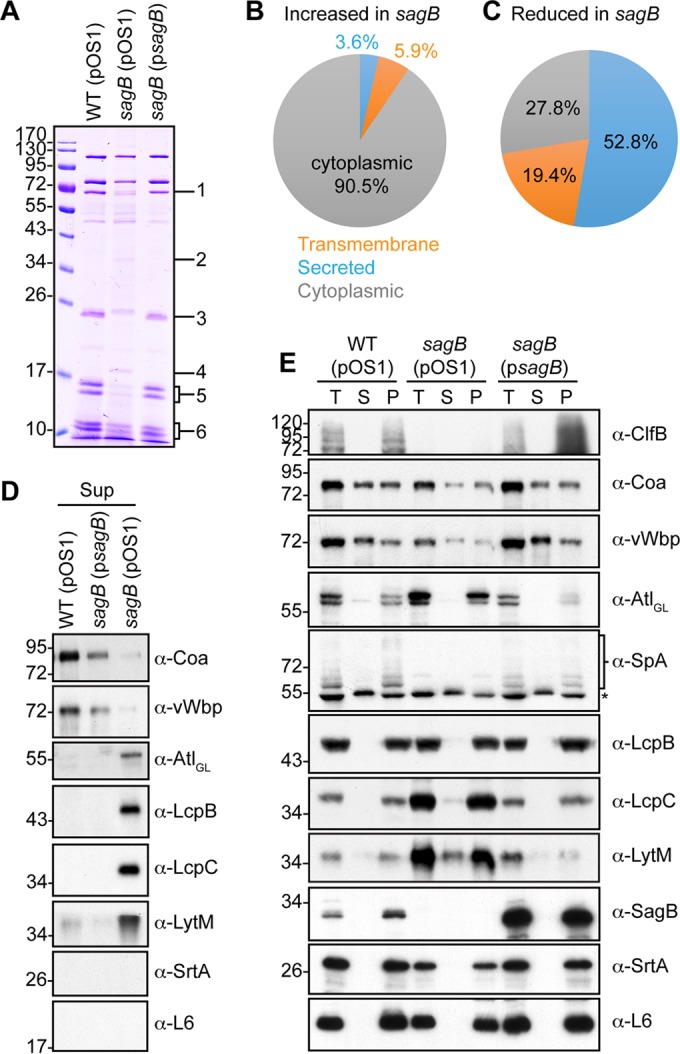
Mutations in the sagB mutant perturb protein secretion in S. aureus. (A) Supernatants of S. aureus wild-type, mutant, and complemented strains cultured to mid-exponential phase (A600 of 0.5) were analyzed for secreted protein on Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gels. Regions of difference in protein abundances in the gel, as indicated by the numbers on the right, were excised for the wild-type (pOS1) and sagB(pOS1) strains for analysis and protein identification by mass spectrometry (Table 2). Protein species in the sagB(pOS1) strain extract displaying at least a 10-fold increase (B) or decrease (C) relative to that of wild type (pOS1) were analyzed for predicted cellular localization using SignalP, version 4.1, and TMHMM, version 2.0, servers. (D) Immunoblots of supernatant samples prepared in the experiment shown in panel A for MALDI-TOF MS. Representative protein species (Coa, vWbp, Atl, LcpB, LcpC, and LytM) were determined by MS to exhibit a difference in abundances in the sagB mutant versus the wild type. Sortase A and ribosomal L6 blots serve as indicators of cell lysis. (E) One milliliter of mid-exponential-phase cultures (A600 of 0.5) was fractionated into total culture (T), supernatant (S), and cell pellet (P) and analyzed for protein content by immunoblotting. The asterisk in the α-SpA panel identifies Sbi.
