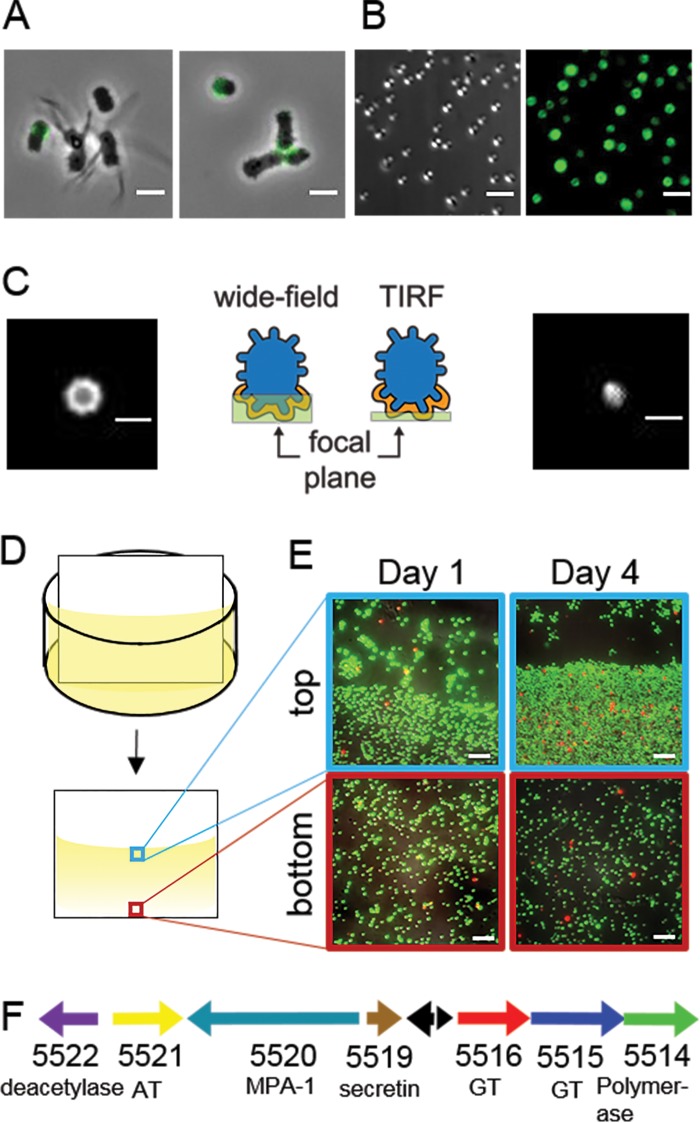
FIG 2.
Short-stalked P. hirschii cells produce a holdfast. (A) A polar polysaccharide is detected by labeling with WGA-AF488 (green) in short-stalked cells but is absent in long-stalked cells. Scale bar = 2 μm. (B) Short-stalked cells with a holdfast attach polarly to a glass surface. A DIC image (left) and fluorescence image of WGA-AF488 signal (right) of attached cells are shown. Scale bar = 2 μm. (C) Wide-field (left) and TIRF (right) images of a holdfast reveal that the holdfast is located at the surface-cell interface and forms a cap around the cell pole. Schematics indicate the focal plane imaged for the wide-field and TIRF images. Scale bar = 1 μm. (D) Schematic of the experimental setup used in the static biofilm assay in panel E. (E) Biofilm attached to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) coverslips stained with the BacLight LIVE/DEAD stain at different times of a static biofilm assay. The images represent overlays of green (live cells) and red (dead cells) collected by epifluorescence microscopy from the meniscus and bottom of the coverslip. Scale bar = 5 μm. (F) Genetic organization of the putative unipolar polysaccharide (upp) gene cluster (C1_5514 to C1_5522). The locus tag numbers and predicted functions are listed below each arrow. Black arrows indicate the positions of hypothetical proteins. AT, acetyltransferase; GT, glycosyltransferase; MPA-1, membrane-periplasmic-auxiliary protein.