Fig. 4.
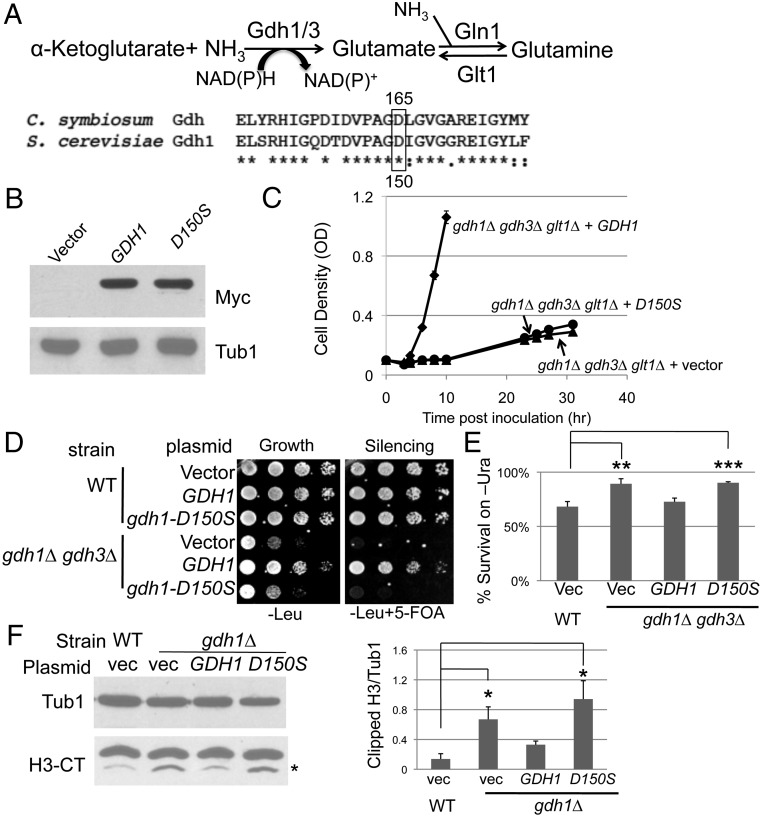
The metabolic activity of the GDH homologs is important for its chromatin functions. (A) The catalytic Asp residue is conserved in S. cerevisiae Gdh1. (Top) The enzymatic reaction catalyzed by the GDH enzymes. (Bottom) Alignment of the C. symbiosum GDH with S. cerevisiae Gdh1. Boxed is the conserved catalytic Asp residue at position 165 in the Clostridium protein. (B) gdh1-D150S-13Myc was stably expressed. gdh1Δ (LPY16026) cells were transformed with vector (pRS316), GDH1-13Myc (pLP2833), or gdh1-D150S-13Myc (pLP2834). Whole-cell extracts were immunoblotted for Myc or Tub1 (loading control). (C) The gdh1-D150S mutant had diminished catalytic activity required to assimilate ammonium. The gdh1Δ gdh3Δ glt1Δ strain (LPY17131) was transformed with vector (pRS315), GDH1 (pLP2631), or gdh1-D150S (pLP2638) and assayed for growth. (D) The conserved Asp residue contributes to Gdh1’s function in telomeric silencing. WT and gdh1Δ gdh3Δ cells were transformed with vector (pRS425), GDH1 (pLP2764), or gdh1-D150S (pLP2698), and telomeric silencing was assessed. (E) Colony counting assay on SC-Ura confirmed the lack of silencing activity of the gdh1-D150S mutant. The assay was described in Materials and Methods. (F) Gdh1’s inhibitory function in H3 clipping is dependent on the conserved Asp residue. Nuclear extracts were prepared from WT (LPY4916) and gdh1∆ (LPY16033) strains transformed with vector (pRS314), GDH1 (pLP3082), or gdh1-D150S (pLP3083) and immunoblotted for H3-CT and Tub1 (loading control). N-terminally clipped H3 was highlighted by the asterisk. Blots from two sets of independent extracts were quantified.