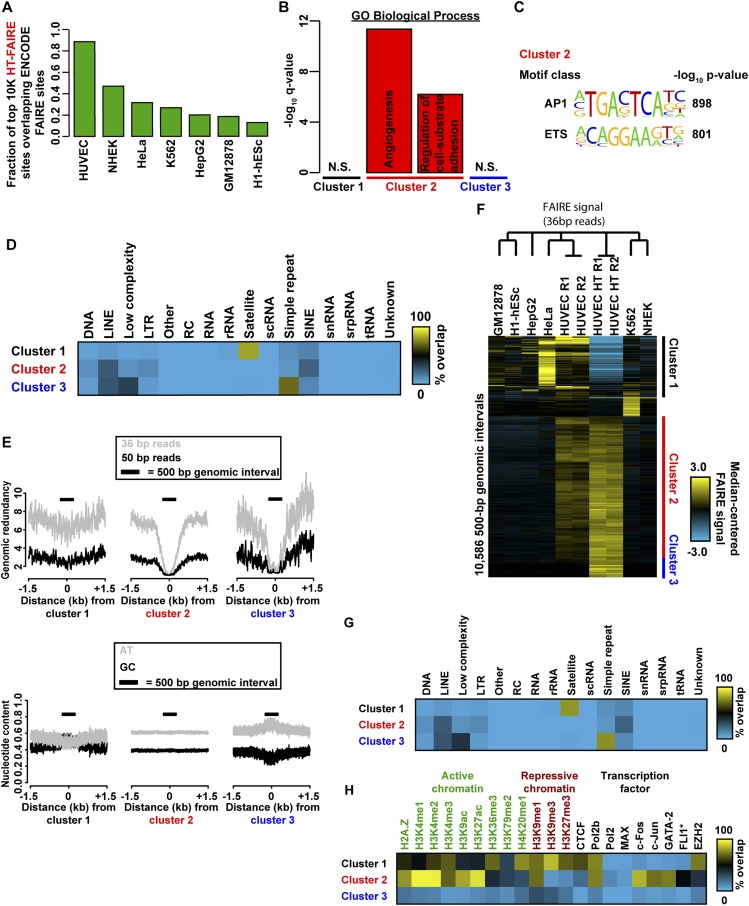
Fig. S2.
Comparison of FAIRE methodologies. (A) Fraction of top 10,000 HT-FAIRE enriched sites overlapping standard FAIRE sites from HUVEC and six other cell types (ENCODE). (B) Ontology enrichment (GREAT) of genes associated with sites in clusters 1–3 (Fig. 1E). (C) Highly enriched TF motifs in cluster 2. Clusters 1 and 3 did not have any motifs determined to be significant by a multicomponent test (Methods). (D) Mappability (Left) and nucleotide content (Right) within 1.5 kb of sites from clusters 1–3 (Fig. 1E). Mappability was assessed for both 36- and 50-bp reads. Genomic redundancy refers to the number of times a given 36- or 50-mer occurs in the reference genome. 500 bp window indicated by bar. (E) Fractional overlap annotation of clusters 1–3 (Fig. 1E) with repetitive element classes. (F) Fractional overlap annotation of clusters 1–3 (H) with histone modifications and transcription factor ChIP-seq peak calls (ENCODE). (G) Fractional overlap annotation of clusters 1–3 (H) with repetitive element classes (RepeatMasker). (H) Hierarchical clustering analysis of ENCODE FAIRE signal in 500-bp intervals from seven cell types, as well as HUVEC HT-FAIRE after truncation of 50-bp reads to 36 bp. Identified clusters exhibit method specificity (clusters 1 and 3) and cell-type specificity (cluster 2).