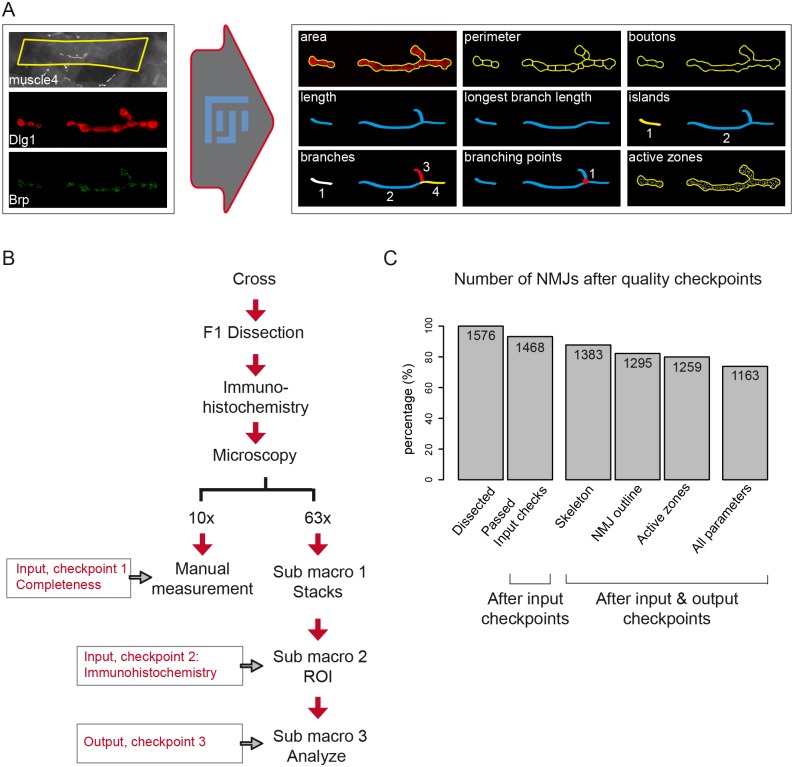
Fig 1. A Fiji macro to systematically quantify NMJ features.
Representation of the Fiji-based macro for NMJ systems analysis (A). The macro was developed using Dlg1 and Brp image stacks as input (left to the arrow). For each NMJ, the indicated nine NMJ features are quantified. The NMJ area, perimeter and boutons are deduced from the NMJ outline and inner segmentations (indicated in yellow). The skeleton (blue) provides the five features total length, longest branch length (sub branches are excluded), the number of Dlg1-based islands (unconnected Dlg1 compartments, in blue and yellow), the number of branches (in different colors), the number of branching points (red dot). The Brp channel is used to count the number of active zones within the NMJ outline (white dots within the yellow outline). The NMJ muscle area is measured at lower magnification by the Fiji freehand selection (yellow box rectangle). NMJs are oriented anterior left, dorsal up. Schematic representation of the NMJ workflow (B). Larvae are dissected and NMJs are stained for Dlg1 and Brp and captured in images at the two magnifications 10x and 63x. Lower magnification snapshots are used to measure the muscle4 area and are simultaneously checked to ensure that the full NMJ is captured at high magnification (= checkpoint 1). Images at high magnification are progressed to stacks and projections in which the region of interest (ROI) is defined to exclusively analyze type 1b NMJs. Images are excluded in checkpoint 2 if the specificity of type 1b cannot be guaranteed or if the quality of the immunohistochemistry is poor. The first two bars of the bar graph (C) represent the amount of NMJs and the percentage that passed the two input checkpoints (93.15%). Sub macro 3 processes the NMJ towards quantitative output and the macro-annotated images are evaluated (= checkpoint 3). Bars three to five represent the percentage of NMJs per threshold that passed the output quality checkpoint (87.75% for the NMJ skeleton; 82.17% for the NMJ outline and 79.89% for Active zones). The final bar represents the percentage of investigated NMJs for which all features were of high quality (73.79%).