Figure 2.
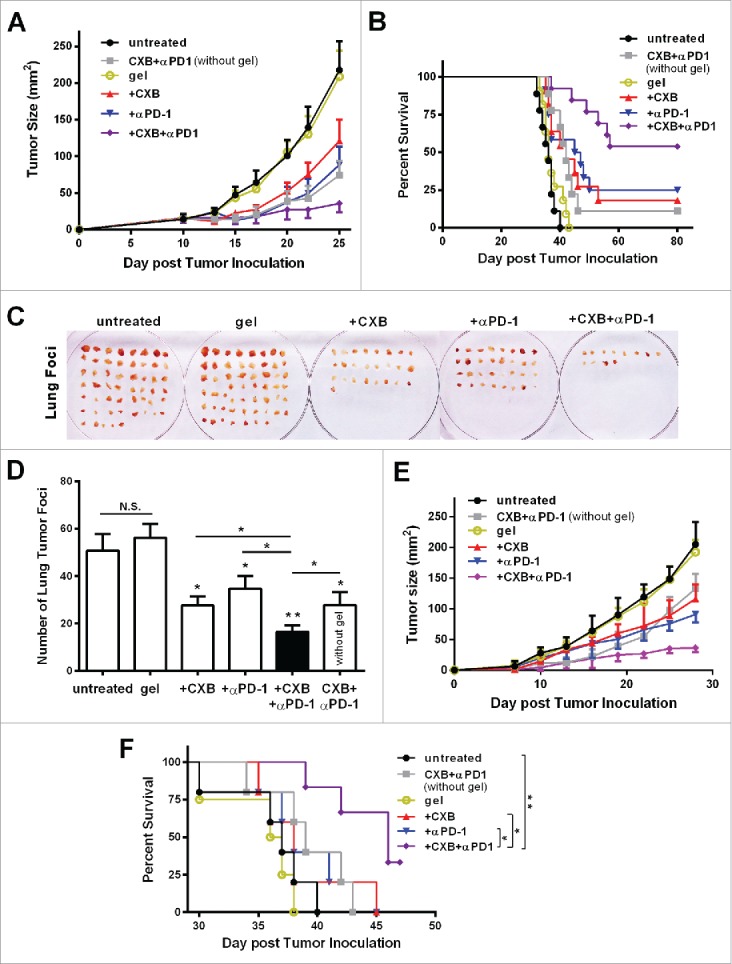
Simultaneous delivery of celecoxib and anti-PD-1 mAb augments their individual inhibitory effects on tumor growth and metastasis. (A and B) C57BL/6 mice received the different treatments at Day 7 after the inoculation of 2.5 × 104 B16-F10 cells. Quantification of the tumor sizes (A) and the survival percentage (B) over time in the animals receiving the non-hydrogel combined therapy of CXB and anti-PD-1 mAb (CXB + αPD-1), the blank hydrogel treatment (gel), and the treatments with the hydrogels delivering CXB (+ CXB), anti-PD-1 mAb (+ αPD-1), or both (+ CXB + αPD-1). n = 9–12 animals per group. Four independent experiments were performed. (C–F) BALB/c mice received the different treatments at Day 7 after the inoculation of 1.0 × 106 4T1 cells. The representative images (C) and quantification (D) of the pulmonary metastatic nodules isolated at Day 32 after tumor cell inoculation from the 4T-1-breast-cancer bearing mice receiving the indicated treatments as in (A) and (B) at Day 7 after tumor inoculation. The primary tumor sizes (E) and the survival percentage (F) in the corresponding treatment groups described in (C). n = 4–6 animals per group. Three independent experiments were performed. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, N.S., not significant, Student's t-tests. The asterisk without a line underneath indicates the comparison to the blank hydrogel group. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.
