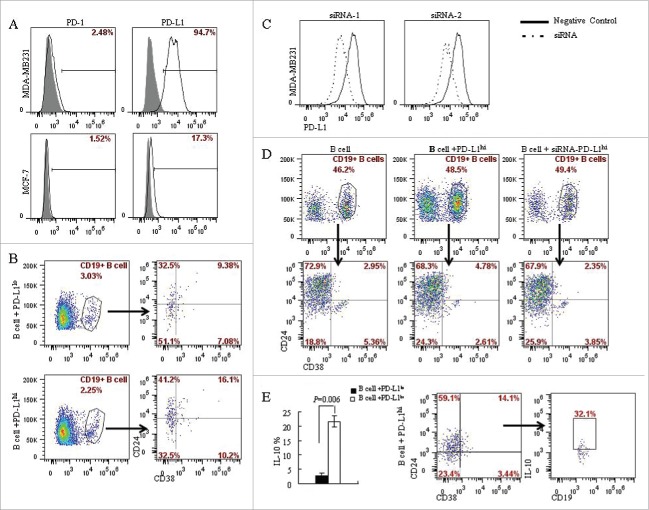
Figure 3.
PD-L1 mediates the differentiation of CD19+ B cells into CD19+CD24+CD38+ B cell subtype. (A) The expression of PD-L1 and PD-1 on breast cancer cell lines was analyzed by flow cytometry. MDA-MB231 expresses high level of PD-L1 (94.7%) compared with MCF-7 (17.3%); Both MCF-7 and MDA-MB231 lacks PD-1 expression. (B) CD19+ B lymphocytes/ breast cancer cells co-culture systems were established to investigate the interaction between PD-L1 expression in breast cancer cells and CD19+ B cells. 16.1% of CD19+CD38+CD24+ B cells were detected in PD-L1hi MDA-MB231, while only 9.38% of CD19+CD38+CD24+ B cells were detected in PD-L1lo MCF-7. (C) To confirmed the relationship between PD-L1 and CD19+ B cells, PD-L1siRNA were used to knockdown the expression of PD-L1. (D) Co-culture of CD19+ B cells and PD-L1hi MDA-MB231 with or without siRNA. The percentage of CD19+CD38+CD24+ B cells were reduced when CD19+ B cells were co-cultured with MDA-MB231 cells with PD-L1 knocked down. (E) A high level of IL10 was detected in PD-L1hi co-culture compared to that in PD-L1lo co-culture system (P < 0.05). And CD19+CD24+CD38+ B cells produced IL-10 following activation by PMA and ionomycin.