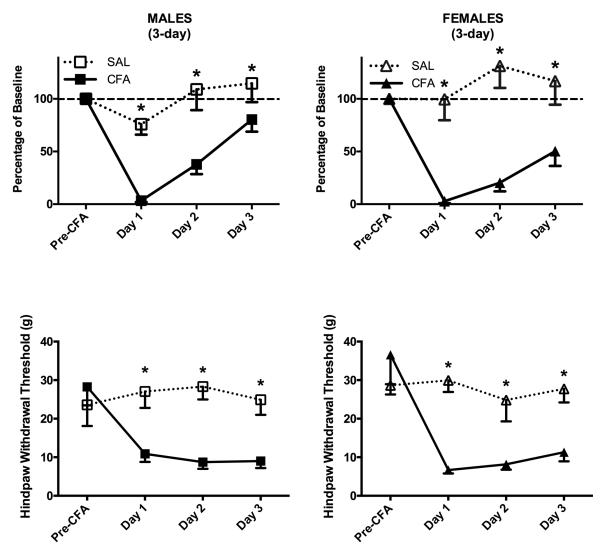
Figure 3. CFA-induced hindpaw inflammation produced depression of wheel running and mechanical allodynia in male and female rats following a 3-day acquisition period.
Top: CFA was injected into the right hindpaw of male and female rats after 3 days of continuous exposure to the wheel in the rat’s home cage. This unilateral inflammation of the hindpaw almost completely inhibited wheel running in male (n = 6) and female (n = 5) rats in the 23 hrs following CFA administration compared to saline-treated control rats (5 male rats; 4 female rats). Wheel running gradually recovered in CFA-treated male and female CFA-treated rats by Day 3. Bottom: Unilateral hindpaw inflammation decreased mechanical withdrawal thresholds in male and female rats compared to non-inflamed control rats. Unlike wheel running, there was no recovery in mechanical thresholds across days. * indicates that groups differ as determined by 95% confidence intervals.