Figure 1.
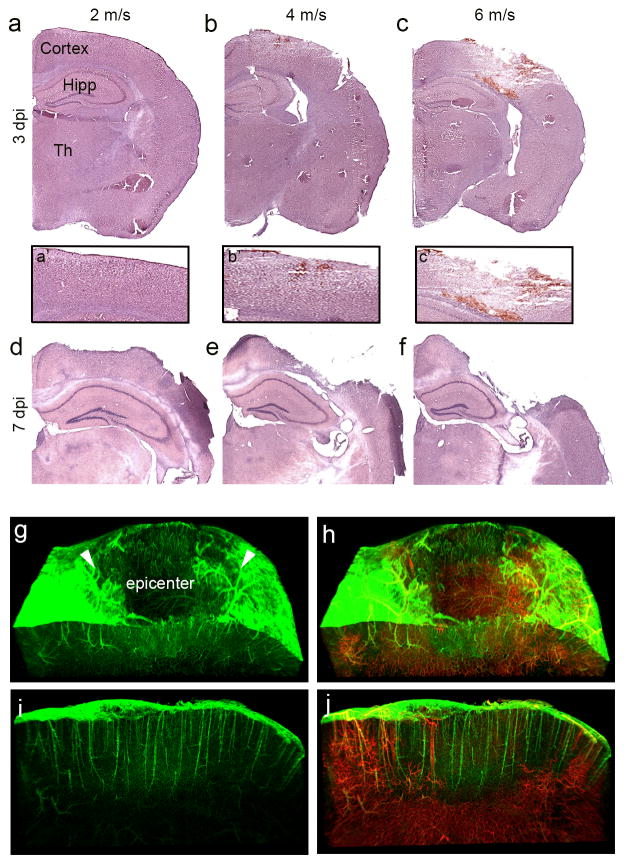
Graded CCI injury leads to graded cortical damage and vascular loss at the injury epicenter. (a–f) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained coronal brain sections at impact velocities of 2 m/s (a, d), 4 m/s (b, e), and 6 m/s (c, f) at 3 (a–c) and 7 (d–f) days after CCI injury (dpi). (a′–c′) Higher magnification H&E stained images of injured cortex. (g–j) Light-sheet 3D images of the CCI injured cortex at 3 dpi in Cdh5-zG mice infused with Lectin-594. Arrowheads depict injury penumbra. Sagittal view of the injury penumbra reveals the presence of ECs (i) but not infusible vessels (j). Hipp, hippocampus, Th, thalamus.