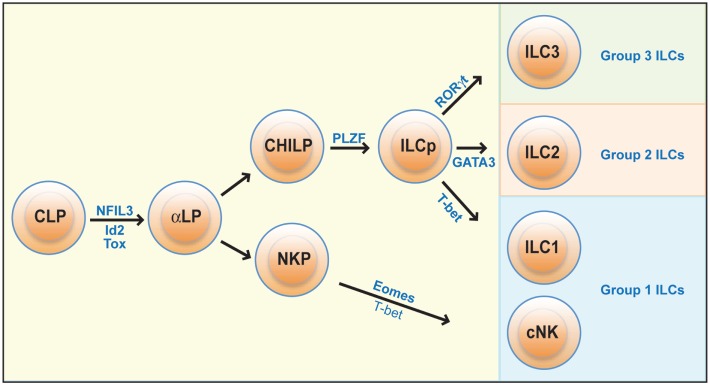
Figure 1.
Development of ILCs. All ILCs develop from a common lymphoid progenitor (CLP), which differentiate into a committed ILC precursor population (αLP). The development of cNK cells then diverges from that of other ILCs: cNK cells arise from an NK cell precursor (NKP), while all other ILCs are formed from a common helper innate lymphoid precursor (CHILP) that upon upregulation of the transcription factors Id2, PLZF, and GATA-3 become committed innate lymphoid cell precursors (ILCp) and can give rise to ILC1s, as well as to most group 2 and 3 ILCs. Development of mature cNK cells from NKPs is critically dependent on the transcription factors Eomes but also involves T-bet, while ILC1 development from ILCp is dependent on T-bet but not Eomes.