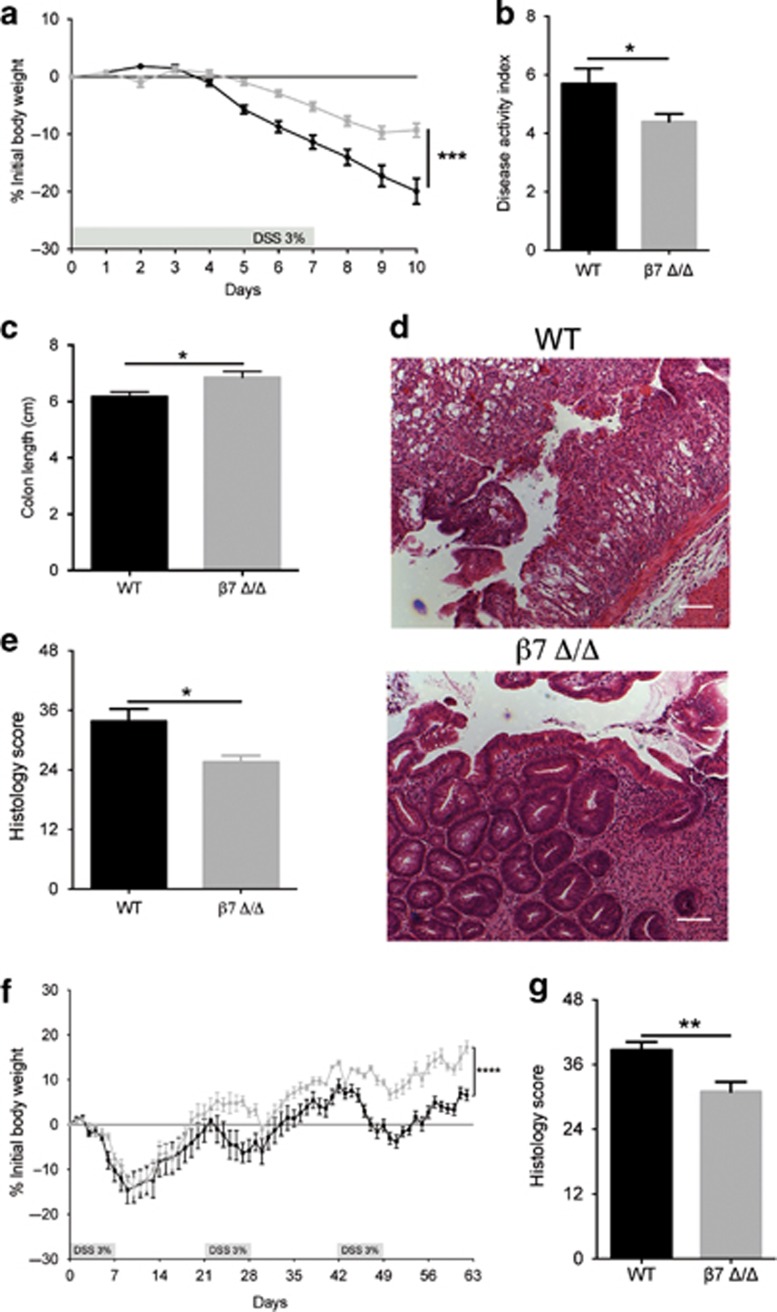
Figure 1.
β7-Integrin deficiency ameliorates acute (a–e) and chronic (f and g) dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis. (a) Percentage of body weight loss (measured daily) of wild-type (WT) (black squares, n=12) and β7-integrin-deficient (β7 Δ/Δ) (gray squares, n=12) mice. (b) Disease activity index (DAI) and (c) colon length from DSS-treated WT (black bar, n=12) and β7 Δ/Δ (gray bar, n=12) mice at day 10 of acute DSS colitis. (d) Representative photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained colon sections from the indicated groups at day 10 of acute DSS colitis at original magnification × 100 (Bar=200 μm). (e) Results of histological scoring of sections from WT (black bar, n=4) and β7 Δ/Δ (gray bar, n=5) mice. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. (f) Percentage of body weight loss (measured daily) of WT (black squares, n=7) and β7 Δ/Δ (gray squares, n=6) mice. (g) Results of histological scoring of sections from WT (black bar, n=7) and β7 Δ/Δ (gray bar, n=6) mice. The data shown are representative of two independent experiments. Data represent mean±s.e.m. Statistical significance was calculated by two-tailed t-test and is indicated as followings: *P<0.05; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.