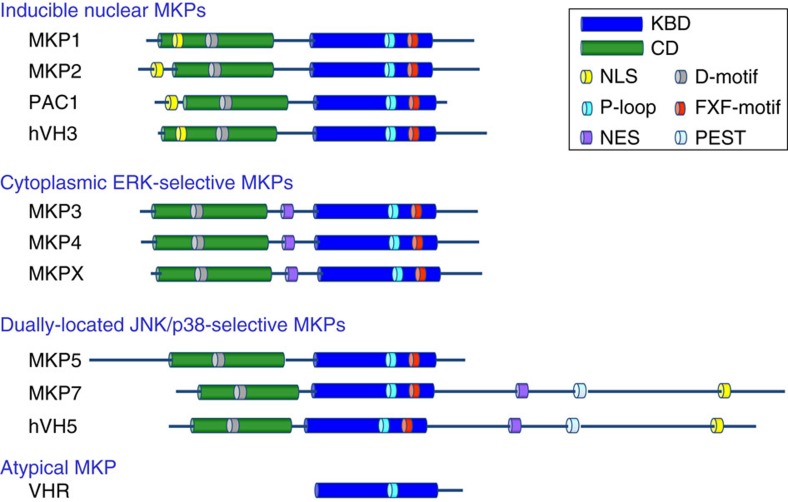
Figure 1. Domain structures of ten human MKPs and the atypical VHR.
On the basis of sequence similarity, protein structure, substrate specificity and subcellular localization, the ten members of MKP family can be divided into three groups. The first subfamily comprises MKP1, MKP2, PAC1 and hVH3, which are inducible nuclear phosphatases and can dephosphorylate ERK (and JNK, p38) MAPKs. The second subfamily contains MKP3, MKP4 and MKPX, which are cytoplasmic ERK-specific MKPs. The third subfamily comprises MKP5, MKP7 and hVH5, which were located in both nucleus and cytoplasm, and selectively inactivate JNK and p38. All MKPs contain both the CD and KBD domains, whereas VHR, an atypical MKP, only contains a highly conserved catalytic domain. In addition to the CD and KBD, MKP7 contains a unique long C-terminal region that contains NES, NLS and PEST motifs, which has no effect on the binding ability and phosphatase activity of MKP7 toward MAPKs. NES, nuclear export signal; NLS, nuclear localization signal; PEST, C-terminal sequence rich in prolines, glutamates, serines and threonines.