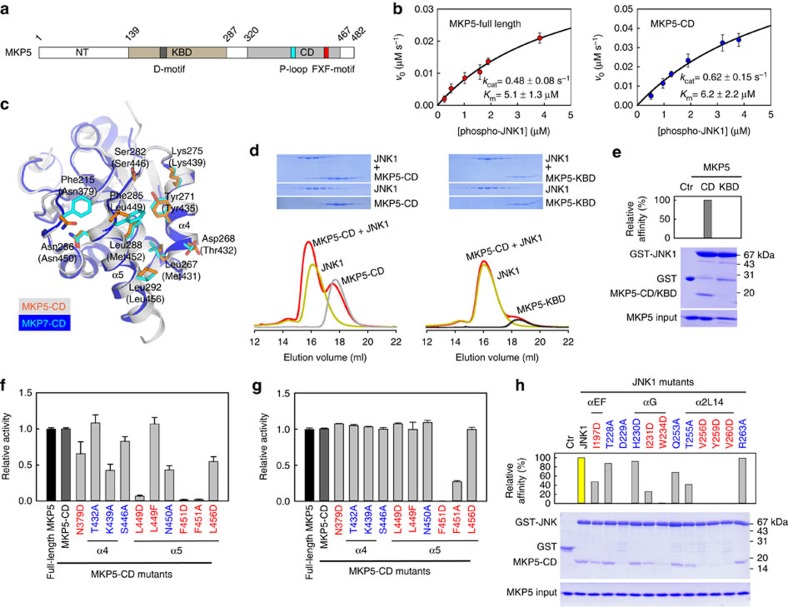
Figure 7. MKP5-CD is crucial for JNK1 binding and enzyme catalysis.
(a) Domain organization of human MKP5. The KBD and CD of MKP5 are shown in brown and grey, respectively. (b) Plots of initial velocity of the MKP5-catalysed reaction versus phospho-JNK1 concentration. The solid lines are best-fitting results according to the Michaelis–Menten equation with Km and kcat values indicated. Each experiment was performed in replicate for at least three times. The error bars represent s.e.m. (c) Structural comparison of the JNK-interacting residues on MKP5-CD (PDB 1ZZW) and MKP7-CD. The corresponding residues on MKP5 are depicted as orange sticks, and MKP5 residues numbers are in parentheses. (d) Gel filtration analysis for interaction of JNK1 with MKP5-CD and MKP5-KBD. (e) GST-mediated pull-down assays for interaction of JNK1 with MKP5-CD and MKP5-KBD. The panels are arranged the same as in Fig. 2d. (f) Effects of mutations in MKP5-CD on the JNK1 dephosphorylation (mean±s.e.m., n=3). (g) Effects of mutations in MKP5-CD on the pNPP hydrolysis reaction (mean±s.e.m., n=3). (h) Pull-down assays of MKP5-CD by GST-tagged JNK1 mutants. The panels are arranged the same as in Fig. 4c.