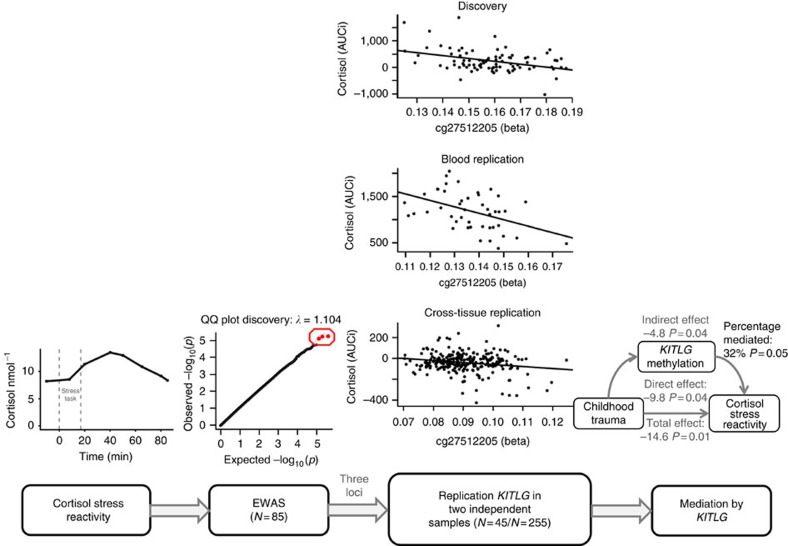
Figure 1. Flowchart of the main analysis.
First we performed a genome-wide analysis of the association between cortisol stress reactivity and DNA methylation in the discovery sample (N=85). On the basis of the P value distribution, we sought replication of the top three loci in two independent samples (N=45/N=255) and replicated the negative association between the top KITLG locus and cortisol stress reactivity. Then we investigated the influence of childhood trauma on KITLG methylation and cortisol stress reactivity in the discovery and blood replication sample. On finding an association for childhood trauma with KITLG methylation and cortisol stress reactivity in the discovery sample and Caucasian of the blood replication sample, we examined whether the KITLG locus is a mediator for the blunted cortisol stress response after childhood trauma exposure.