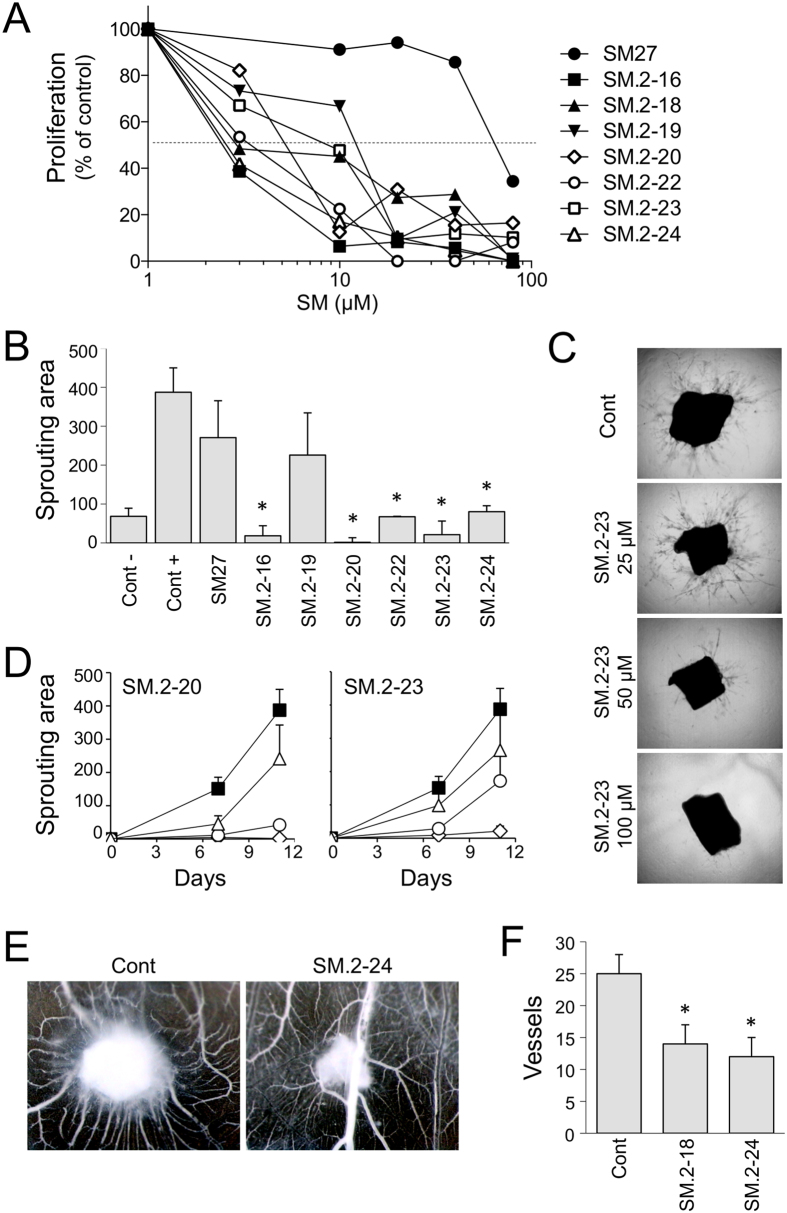
Figure 4. Biological activity of the selected hits.
(A) Endothelial cell proliferation. BAEC were exposed to FGF2 (5 ng/ml) with increasing concentrations of molecules (3–80 μM). After 72 h, cells were stained and proliferation measured as absorbance. Data are the percentage of control proliferation (in absence of molecules), mean of value from 2 experiments performed in triplicate. (B–D) Aortic ring assay. Sections of murine aortas were embedded in Matrigel, in the presence of FGF2 (30 ng/ml) and the indicated small molecule. The formation of capillary structures sprouting from the rings was analyzed after 7 and 11 days as described in Methods, and the angiogenic response expressed as area covered by the sprouting structures (arbitrary units, mean and SE, n ≥ 6). (B) Antiangiogenic activity of the small molecules (100 μM). (C) Examples of time-dependent and dose-dependent effect of two compounds (SM.2–20 and SM.2–23), tested at 100 (diamond), 50 (circle) and 25 μM (triangle) compared to control (black squares). (D) Representative pictures of sprouting from control and SM.2–23 treated aortic sections. Original magnification, 20x. (E,F) Chorioallantoic membrane assay. FGF2 (200 ng) was administered in the absence or presence of the indicated compound (0.5 μg) on day 8 (n = 10). (E) Angiogenic response is evaluated 4 days later, and expressed as number of vessels entering the sponge (mean and SD). (F) Representative pictures are shown. Original magnification, 50x.