Abstract
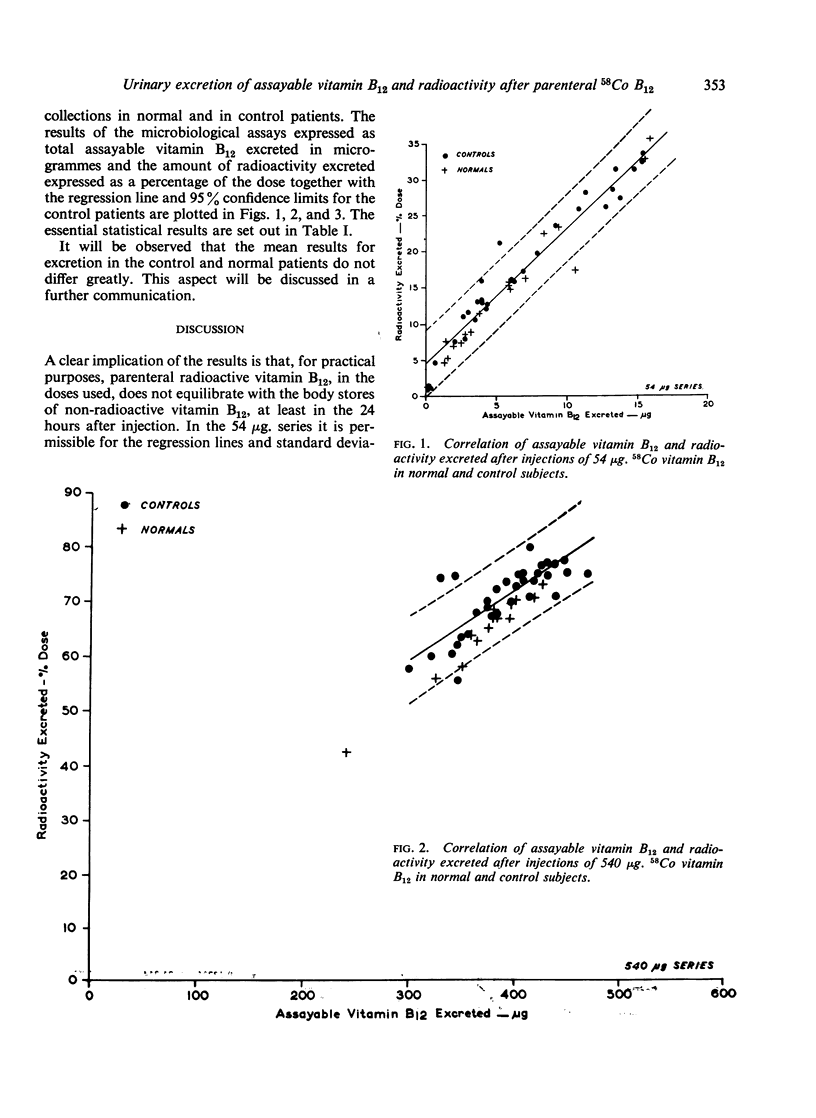
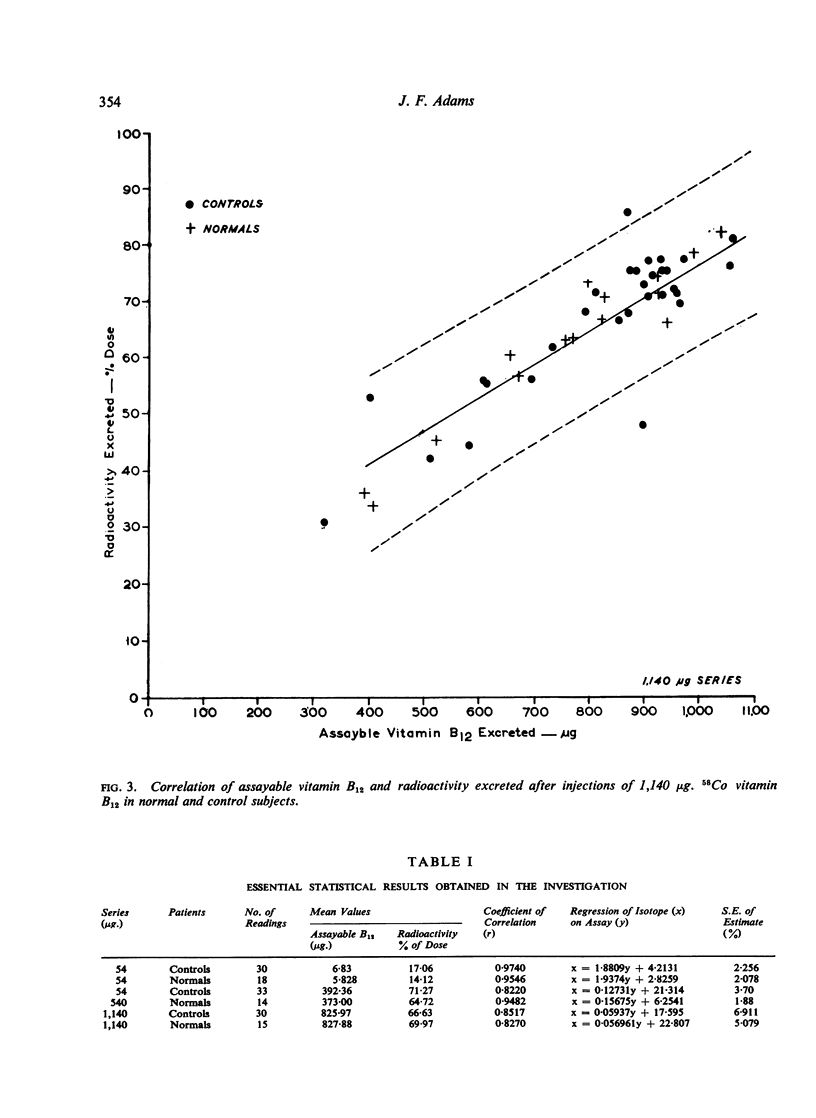
Evidence is presented that after injection of radioactive vitamin B12 in man, there is a close correlation between the amount of radioactivity excreted and the amount of assayable vitamin B12 excreted, and thus that the amount of radioactivity excreted is a true measure of the vitamin B12 excreted. The possible reasons for this occurrence are discussed and it is suggested that in the body vitamin B12 does not exist as such but as an analogue or active derivative.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ROSS G. I. M. Vitamin B12 assay in body fluids using Euglena gracilis. J Clin Pathol. 1952 Aug;5(3):250–256. doi: 10.1136/jcp.5.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILLING R. F. Intrinsic factor studies II. The effect of gastric juice on the urinary excretion of radioactivity after the oral administration of radioactive vitamin B12. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Dec;42(6):860–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach H., Toohey J., Barker H. A. ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF B(12) COENZYMES CONTAINING BENZIMIDAZOLE OR DIMETHYLBENZIMIDAZOLE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Apr;45(4):521–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.4.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


