Figure 5.
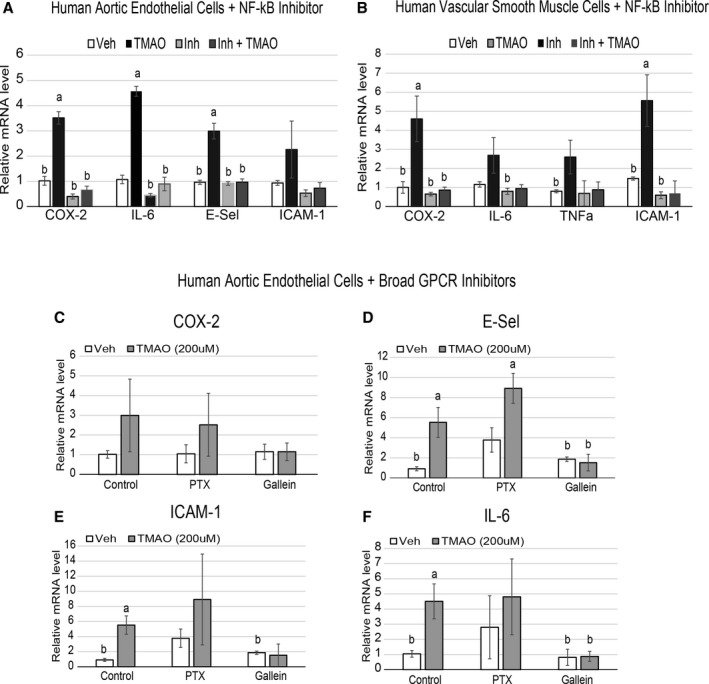
NFkB and Gßγ signaling is required for TMAO‐induced inflammatory gene expression in endothelial and smooth muscle cells. A and B, HAECs (A) or vascular smooth muscle cells (B) were pretreated for 30 minutes with control (DMSO) or 100 nmol/L NFkB activation inhibitor followed by an overnight treatment with or without 200 μmol/L TMAO and probed by qPCR for inflammatory gene expression (n=6). ANOVA with a Tukey post hoc test was used with TMAO and inhibitor as the 2 factors. We did not observe interaction between inhibitor and TMAO groups. C through F, HAECs were pretreated for 1 hour with control (DMSO), 200 ng/mL PTX, or 10 μmol/L Gallein, followed by addition of vehicle (PBS) or 200 μmol/L TMAO, then probed by qPCR for inflammatory gene expression. All experiments were confirmed in at least 3 separate donors, and qPCR genes normalized to RPL13A expression. a P<0.05 compared with vehicle‐alone group; b P<0.05 compared with TMAO‐alone treatment group. COX‐2 indicates cyclooxygenase 2; E‐Sel, E‐selectin; HAEC, human aortic endothelial cell; IL‐6, interleukin 6; NFkB, nuclear factor‐κB; PTX, pertussis toxin; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TMAO, trimethylamine N‐oxide; TNF‐a, tumor necrosis factor α; Veh, vehicle.
