Figure 11.
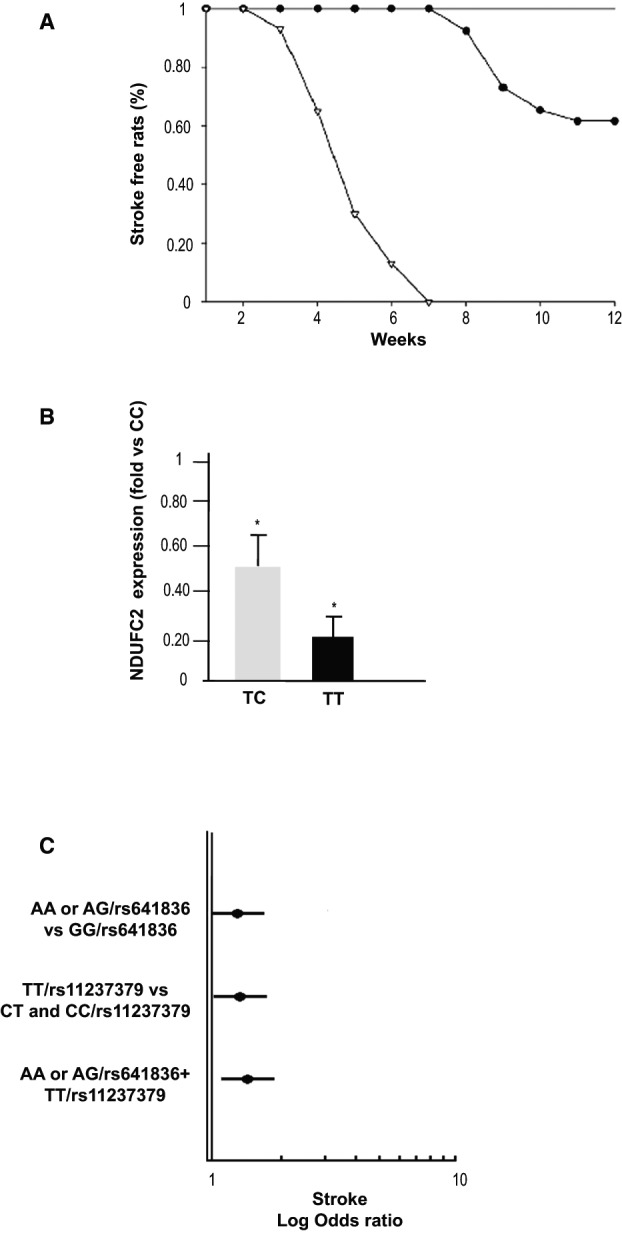
Ndufc2‐related stroke phenotype in both animal models and in humans. A, Stroke occurrence in heterozygous SHR‐Ndufc2 em2Mcwi line as compared to SHRSP and to all other lines (SHRSR, wild‐type SHR‐Ndufc2 em2Mcwi, heterozygous, and wild‐type SHR‐Ndufc2 em1Mcwi). Comparison of heterozygous SHR‐Ndufc2 em2Mcwi versus SHRSR and all SHRSR‐derived lines was significantly different (P<0.002). Comparison of heterozygous SHR‐Ndufc2 em2Mcwi versus SHRSP was significantly different (P<0.001). For numbers of animals included in these studies, see Table 1. Symbols: open triangles=SHRSP; closed circles=heterozygous SHR‐Ndufc2 em2Mcwi; straight line includes: SHRSR; wild‐type and heterozygous SHR‐Ndufc2 em1Mcwi, wild‐type SHR‐Ndufc2 em2Mcwi. B, NDUFC2 expression assessed by RT‐PCR in peripheral blood lymphocytes in a cohort of young healthy subjects carrying wild‐type (n=6), heterozygous (n=12), and double‐mutant (n=6) genotypes for NDUFC2/rs11237379. *P<0.0001 for both CT and TT versus CC wild‐type genotype (t test analysis). Values in the figure are expressed as means±SD. C, Plot showing the logarithmic ORs for stroke in A allele carriers at rs641836, TT genotype carriers at rs11237379, and A/rs641836+TT/rs11237379 carriers with respect to the other genotypes of NDUFC2 tagSNPs (at multivariable logistic regression analysis). OD indicates odds ratio; RT‐PCR, reverse‐transcriptase polymerase chain reaction; SHRSP, stroke‐prone spontaneously hypertensive rat; SHRSR, stroke‐resistant SHR.
