Fig. 3.
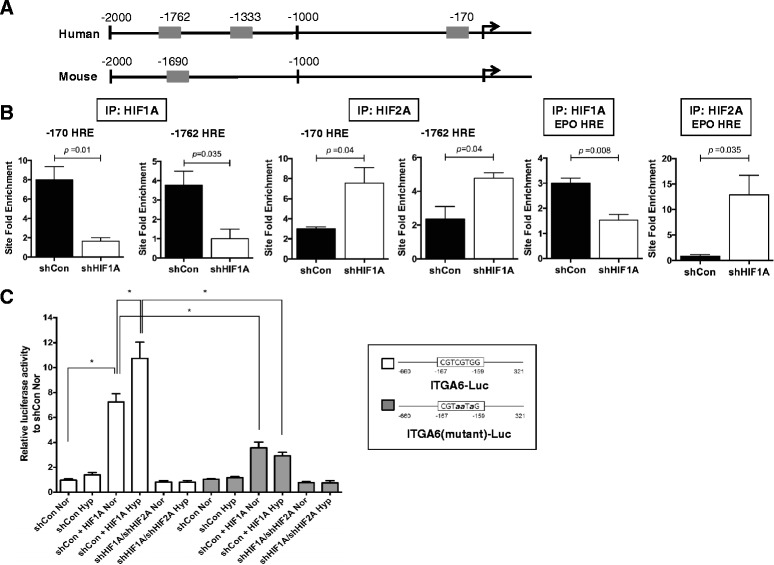
ITGA6 is a direct HIF transcriptional target gene. a A schematic representation of putative HREs identified in the proximal promoter of ITGA6 that were assessed for HIF-1α and/or HIF-2α recruitment by ChIP assays. b MDA-MB-231 shControl and shHIF1A cells were cultured at hypoxia (0.5 % O2) for 6 h, and chromatin fragments were immunoprecipitated using HIF-1α or HIF-2α antibodies or anti-rabbit IgG (as the non-specific binding control). SYBR Green-based qRT-PCR was conducted on the purified, isolated DNA fragments to determine the site fold enrichment of HIFα recruitment relative to signal detected in the anti-rabbit IgG control per genotype (qRT-PCR values observed for the IgG control were set to 1.0 per genotype). As the positive control, qRT-PCR was also performed using primers flanking a previously validated, functional HRE site in the 3’ EPO enhancer. Each panel shows the mean site fold enrichment ± SEM of technical replicates; data presented are representative of three replicate experiments. c Luciferase reporter assays were used to compare relative luciferase activity between MDA-MB-231 shControl or shHIF1A/shHIF2A cells transiently transfected with a wild type ITGA6 promoter linked to luciferase (ITGA6-Luc; white bars) or a HRE mutant promoter construct [ITGA6 (mutant)-Luc; grey bars] and then cultured at normoxia (Nor) or hypoxia (Hyp). In some cases, a stabilized version of murine HIF-1α was also co-transfected (+HIF1A). The mean ± standard deviation are shown; p <0.05 by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. The mutant ITGA6 promoter contains three point mutations within the HIF consensus site
