Figure 7.
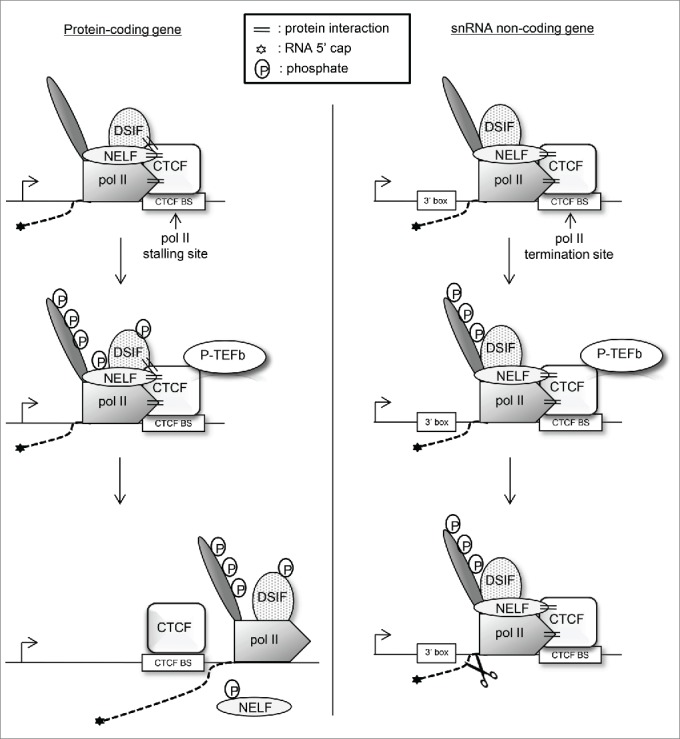
Model for the role of CTCF in the regulation of RNAP II transcription elongation. CTCF bound to its binding site (BS) at early elongation checkpoint or termination sites increases recruitment or stabilization of NELF and DSIF to enhance RNAP II stalling/termination. On protein-coding genes, recruitment of DSIF but not NELF is required for stalling. Recruitment of P-TEFb requires CTCF and phosphorylation converts DSIF from a repressor to an activator, RNAP II phosphorylation activates downstream RNA processing and elongation, whereas phosphorylated NELF leaves the elongation complex. CTCF therefore both help to set up an early elongation checkpoint and allow RNAP II to negotiate the checkpoint while promoting the recruitment of chromatin remodeling, elongation, and RNA processing factors. On an snRNA gene instead, CTCF helps to recruit NELF to cause termination of transcription and P-TEFb to phosphorylate the RNAP II CTD to activate efficient recognition of the 3’ box, thereby linking these 2 processes.
