Figure 1.
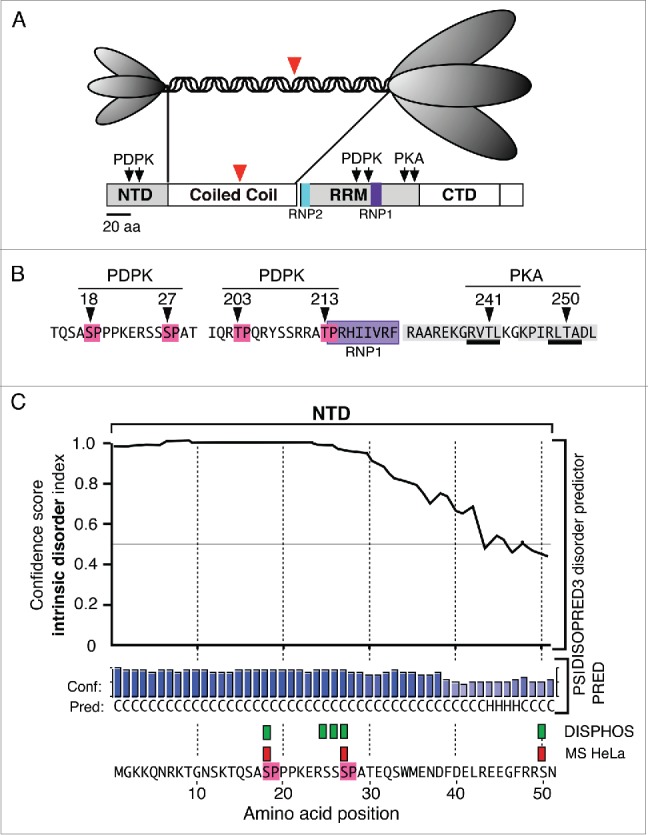
Structural Features of ORF1p (A). The top panel illustrates the trimeric structure of the protein revealed by atomic force microscopy13 and the domains present in the monomer: N-terminal domain (NTD), coiled coil domain, RNA recognition domain (RRM), the C-terminal domain (CTD). The ovals that correspond to the NTD and the C-terminal half of the trimer cartoon are scaled to the their relative masses. The large red arrowheads indicate the amino-terminus of the protein that was expressed in E. coli for crystallization.25 (B) The arrows indicate the locations of phosphokinase target sites and the amino acids corresponding to the PDPK sites are highlighted in red, those comprising the RNP1 motif in purple, those making up the PDPK docking sites in gray, and those corresponding to the PKA target sites are underlined in black. C. The results generated by the DISOPRED, PSIPRED and DISPHOS predictions programs (see text). The green rectangles correspond to the DISPHOS predictions for phosphorylated serines, the red rectangles correspond to those found by mass spectroscopy on ORF1p expressed in HeLa cells.
