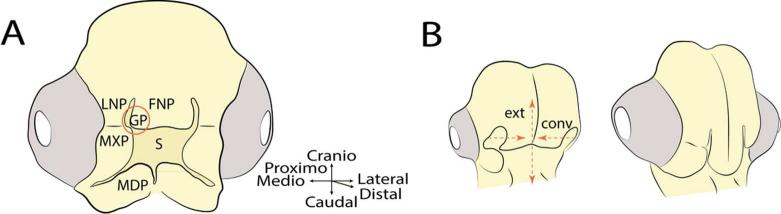
Fig. 1.
Morphology of the face of the chicken embryo. (A) A schematic representation of a chicken embryo at approximately HH24-26. At this time, the facial anlagen are apparent surrounding the stomodeum (S). The upper jaw forms from the paired Maxillary Prominences (MXP), the paired Lateral Nasal Prominences (LNP) and the median Frontonasal Prominence (FNP). The lower jaw forms from the paired Mandibular Prominences (MDP). The globular processes (GP) form the lateral edges of the FNP and will fuse to the MXP and LNP to form the early primary palate (red circle). (B) After fusion of the facial primordia, the facial tissues converge toward the midline (conv) and extend along the craniocaudal axis (ext). These morphogenetic changes make the face appear to undergo a convergent-extension-like pattern of growth (drawn from Hu et al. (2015).