Fig. 2.
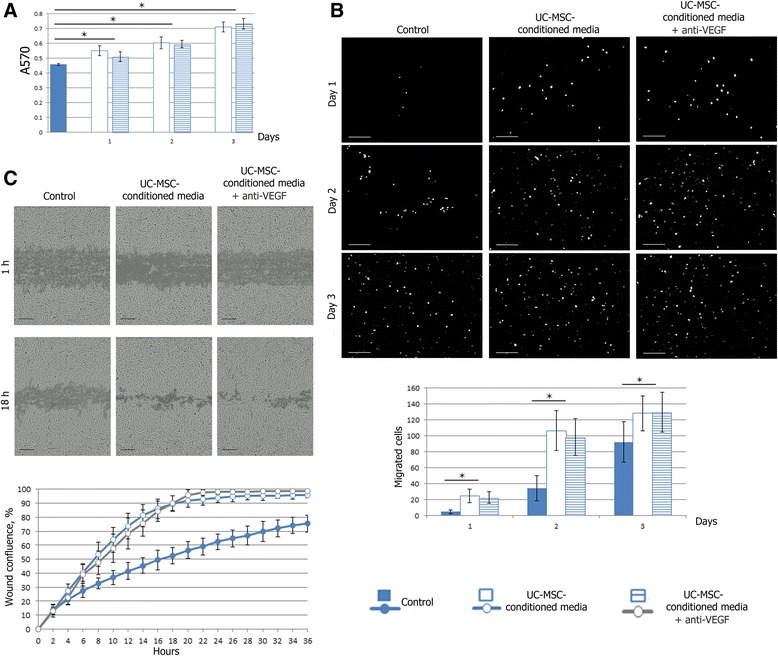
Effects of UC-MSC-conditioned media on proliferation, directed migration, and motility of EA.hy926 cells. a Effects of UC-MSC-conditioned media on proliferation of EA.hy926 cells was determined by MTT assay. Cells were treated with UC-MSC-conditioned media or UC-MSC-conditioned media supplemented with anti-VEGF antibody for 1, 2, or 3 days. Control cells were treated with growth media for 3 days. Values are expressed as average ± SD of three replicates. *p <0.05. b Migration of EA.hy926 cells to UC-MSC-released chemoattractants was measured by transwell chamber migration assay. UC-MSCs were seeded in the lower part of transwell plates, while EA.hy926 cells were placed in the upper chambers. (Upper) Representative images of EA.hy926 cells, which migrated to the other side of the membrane and were stained with DAPI. Scale bar 200 μm. (Lower) Quantification of transwell chamber migration assay. Values are expressed as average ± SD of three replicates. *p <0.05. c Effects of UC-MSC-conditioned media on motility of EA.hy926 cells was analyzed using wound healing assays. (Upper) Representative images of an in vitro scratch wound healing assay in EA.hy926 cells in the presence of UC-MSC-conditioned media or UC-MSC-conditioned media supplemented with anti-VEGF antibody, vs. growth media. Scale bar 200 μm. (Lower) Quantification of in vitro wound healing. Values are expressed as average ± SD of three replicates. There was a significant increase in the wound confluence exposed to UC-MSC-conditioned media or UC-MSC-conditioned media supplemented with anti-VEGF antibody compared with growth media at 8 hours after scratching. h hours, UC-MSC umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cell, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor
