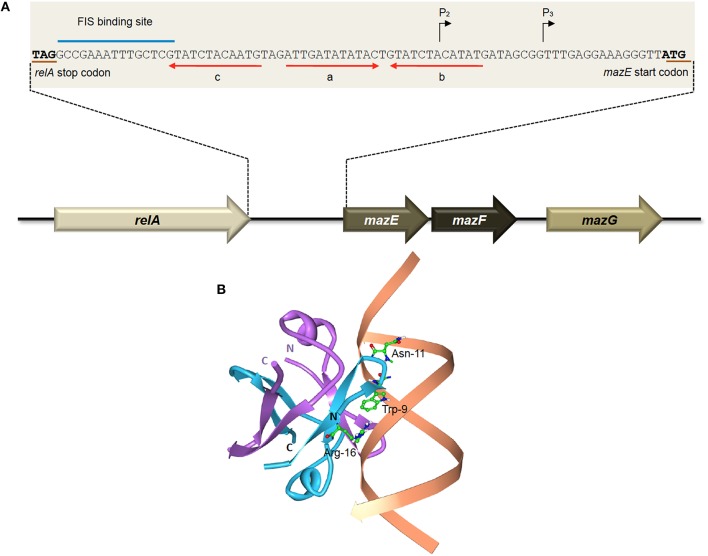
Figure 2.
The E. coli-encoded MazEF TA system. (A) Genetic organization of the E. coli mazEF operon, and the regulatory elements on the mazEF promoter. Black arrows denote the transcriptional start sites of promoters P2 and P3. The stop codon of RelA and the start codon of MazE are underlined in brown. The FIS binding site is indicated with a blue line. Alternating palindromic regions “c-a” or “a-b” are indicated with red arrows. Adapted and modified from Marianovsky et al. (2001). (B) Structure of the MazE1−50 antitoxin homodimer-DNA complex (PDB accession: 2MRU). The MazE1−50 homodimer is indicated in blue and purple with the operator DNA indicated in orange. The N- and C-termini of the two MazE1−50 units are as labeled. The key amino acid residues of MazE that are involved in binding to the major groove of the double-stranded “a” operator DNA, i.e., Trp-9, Asn-11, and Arg-16 (Zorzini et al., 2015), are shown for one of the MazE monomers (blue).