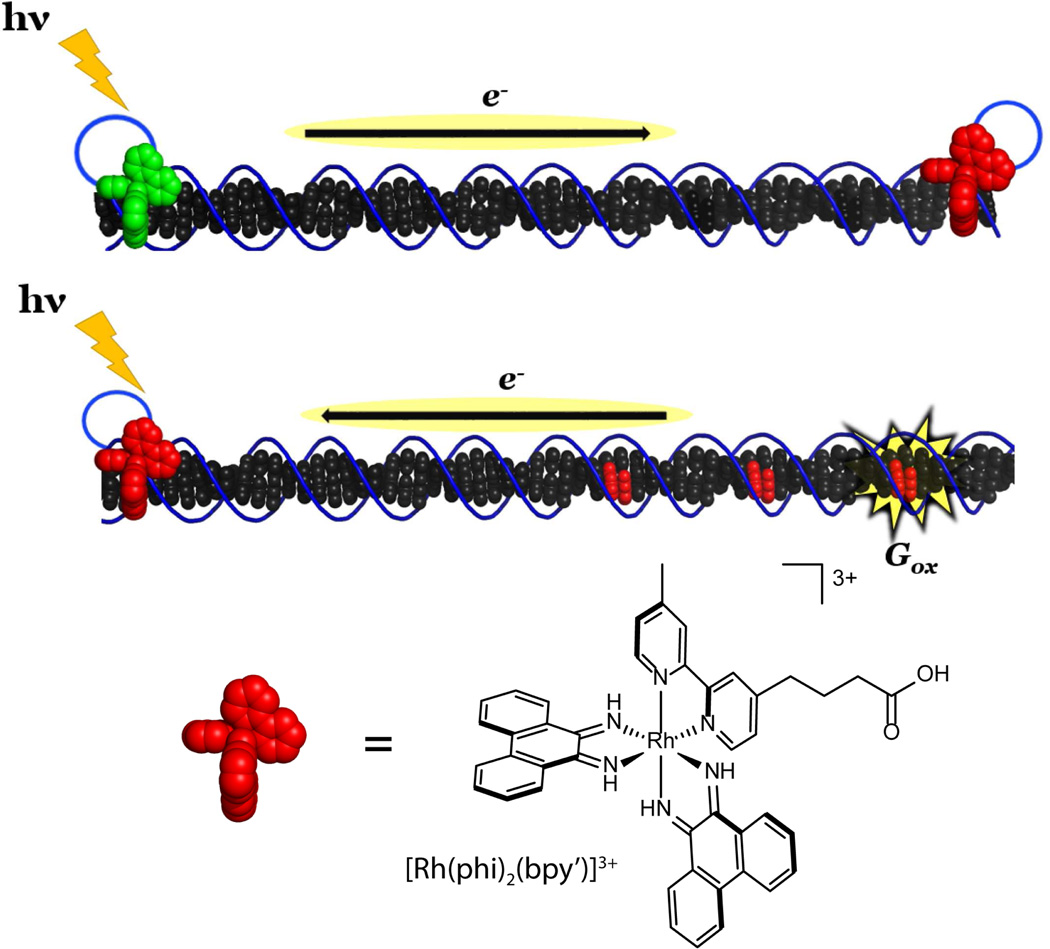
Figure 2. Solution platforms for studying DNA CT.
Top: In the initial studies of DNA CT, electron transfer between metal complexes via the DNA could be detected by monitoring the quenching of the fluorescence from a tethered ruthenium metal complex (green) by a distally tethered rhodium complex (red). Bottom: DNA CT can also be detected by monitoring the oxidation of guanine by a tethered rhodium photooxidant (red) injecting holes into the DNA that localize to the distal guanines. Structure of an intercalating photooxidant [Rh(phi)2(bpy′)]2+ is shown.