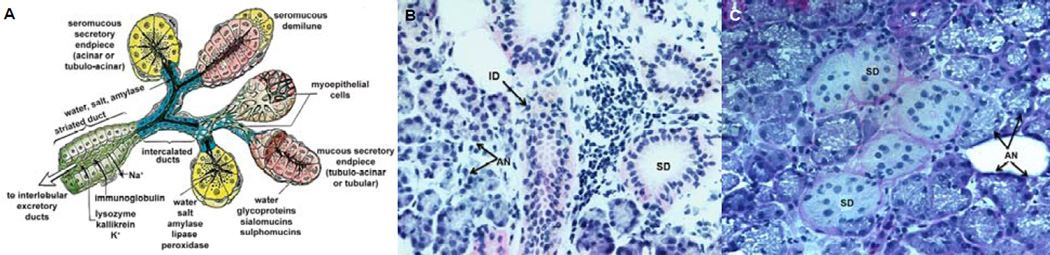
Figure 1.
Structure and organization of the human salivary gland. (A): Schematic illustration of the cross-sectional view of the salivary gland composed of the serous acinus and the intercalated duct (adapted from Gray et al, 199593 with permission). (B): Hematoxylin and eosin staining of human salivary gland tissue (20×). (C): Periodic acid Schiff staining of the salivary gland tissue (40×). Arrows point to AN, acini; AC, acinar cells; ID, intercalated duct; SD, striated ducts; and DC, ductal cells.