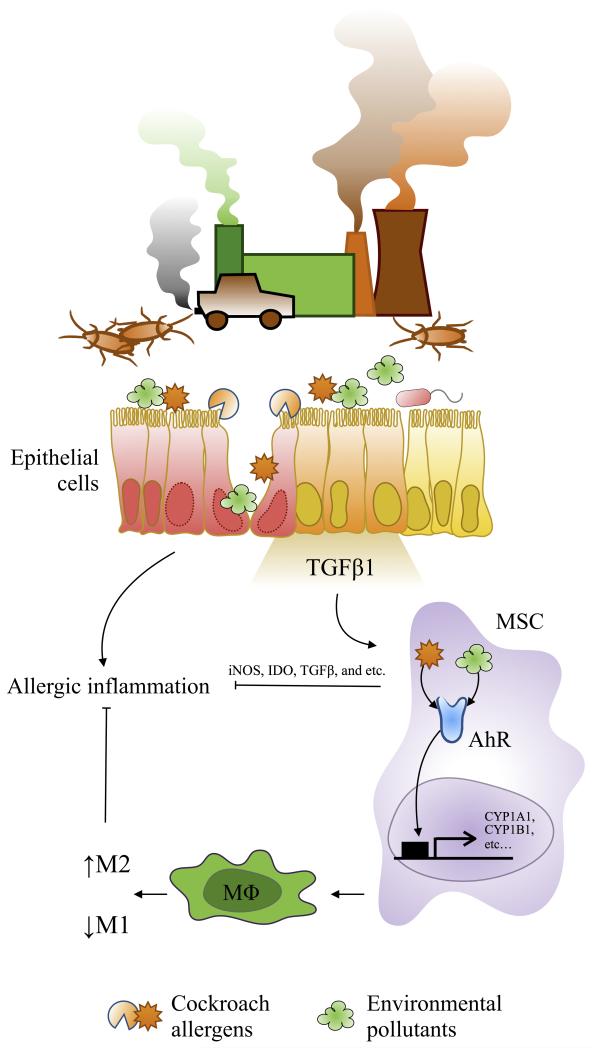
Figure 4.
Proposed model in the role of AhR in modulating environmental pollutant and allergen-induced allergic inflammation. Airway epithelial cells can be damaged after exposure to environmental pollutants and cockroach allergens and release cytokines and chemokines (e.g., TGFβ1), which can recruit MSCs and some other inflammatory cells to the epithelial damaged sites for tissue repairing/inflammation. The recruited MSCs activated through AhR by environmental pollutants or cockroach allergens or both synergistically release anti-inflammatory factors (e.g., iNOS, IDO, and TGFβ1) and suppress airway inflammation. On the other hand, activated MSCs may modulate macrophage differentiation through AhR and inhibit airway inflammation. MSC: mesenchymal stem cell, AhR: aryl hydrocarbon receptor, MΦ: macrophage, M1: classically activated macrophage, M2: alternative activated macrophage, IDO: indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.