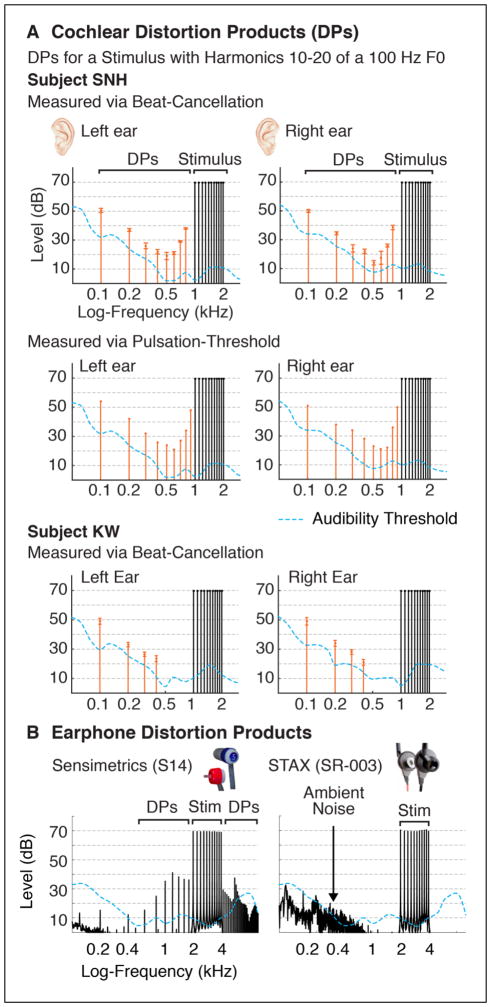
Figure 1. Illustration of Cochlear and Earphone Distortion Products.
A. Examples of distortion products (orange points) resulting from nonlinearities in the cochlea’s response to sound. The sound stimulus contained energy only at harmonics 10–20 of a 100 Hz F0 (black points), but audible DPs were generated at many lower harmonics. DPs were measured psychophysically using the beat-cancellation technique in two subjects, and the pulsation-threshold method in one subject (see Methods). Pure-tone audibility thresholds are plotted for comparison. Error-bars for the beat-cancellation measurements indicate the range of cancellation-tone levels that removed audible beating. B. Examples of distortion products resulting from earphone nonlinearities. Each figure plots the spectrum of the audio waveform produced by an earphone for a stimulus composed of harmonics 10–20 of a 200 Hz F0. Sensimetrics earphones, commonly used in auditory neuroimaging, produced audible DPs at frequencies not in the original stimulus. STAX earphones produced no measurable DPs for the same stimulus.