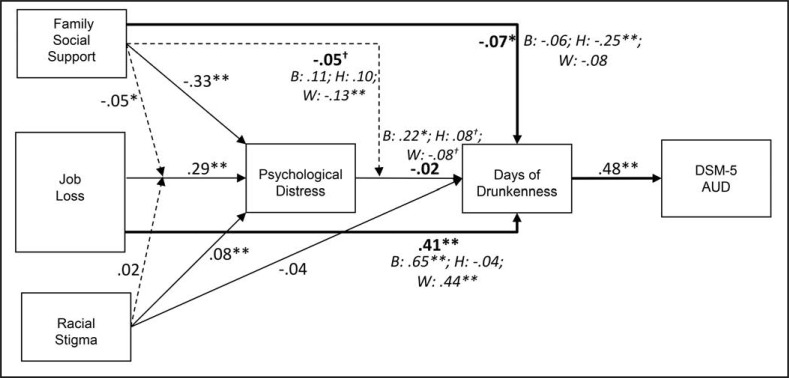
Figure 1.
Standardized coefficients from overall model, with significant racial/ethnic differences indicated in bold and italic. B = Black/African American, including Hispanic Blacks; H = Hispanic; W = White; DSM-5 = Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition; AUD = alcohol use disorder. Demographic controls included race/ethnicity, age, income, education, gender, alcohol problems priorto recession, and parental alcoholism. Interactions of job loss with stigma and social support (and with social support and distress) are indicated with dashed lines. Significant indirect effects are indicated with bold lines. Model fit statistics: root mean square error of approximation = .027; comparative fit index = .904; Tucker-Lewis index = .753. †p < .10; *p < .05; **p < .01.