Fig. 1.
Optimization of the targeted exome approach.
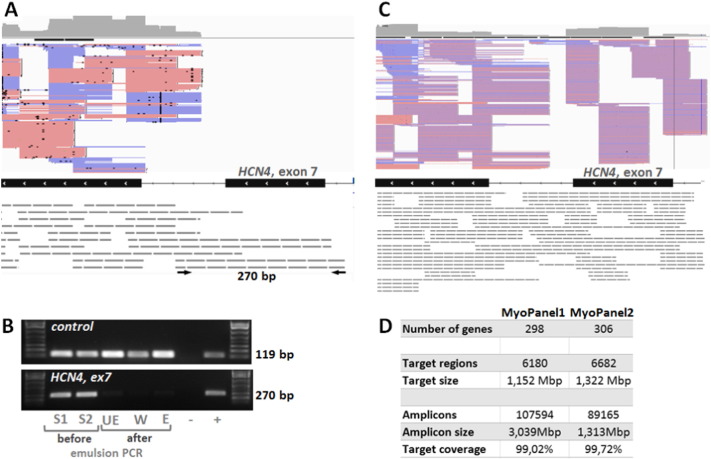
A. IGV visualization of MyoPanel1 HaloPlex probes (grey dashed lines) covering the exons 7 and 8 of HCN4 gene. Pink and blue lines correspond to reads (forward and reverse respectively) obtained from the sequencing experiment. Both longer and shorter HaloPlex probes cover exon 8, generating a number of reads. Only longer (280 bp and more) probes cover exon 7, producing no reads. PCR primers specific to the 280 bp probe are shown as black arrows. B. Longer HaloPlex probes are lost during the emulsion PCR step. PCR using individual probe-specific primers was performed on aliquots from the following library preparation steps: two different samples before emulsion PCR (S1 and S2), before enrichment (UE), wash solution after elution (W), after enrichment (E). A PCR fragment (119 bp) is amplified using primers specific to a shorter 157 bp control probe, while no PCR fragment is produced from post-emulsion PCR steps library aliquots using primers specific to a 280 bp probe (HCN4, exon 7). Similar results were obtained for three other longer probes. C. IGV visualization of the same region as shown in A for the targeted exome MyoPanel2. Shorter HaloPlex probes cover exon 7, producing a number of reads. D. Characteristics of MyoPanel1 and 2 designs.