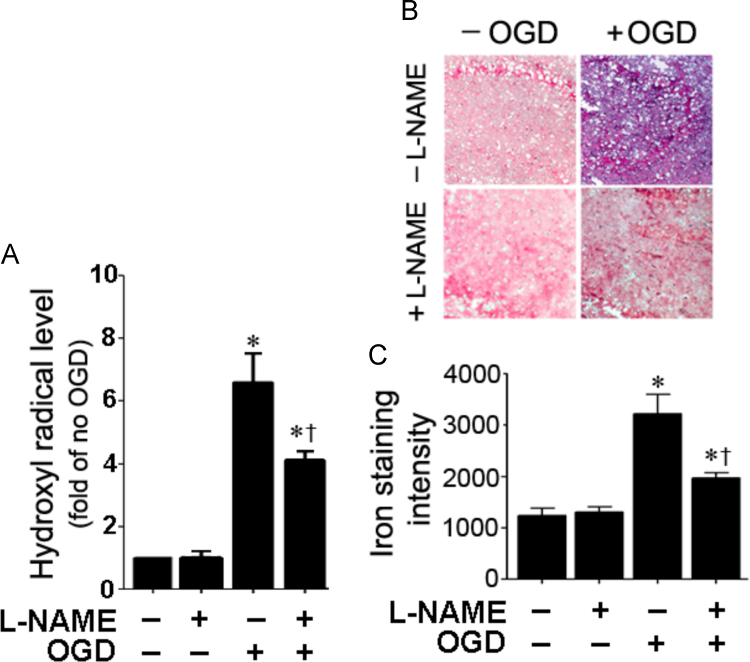
Fig. 2.
NO inhibition attenuates hydroxyl radical generation and reduces iron deposition in rat hippocampal slice cultures exposed to oxygen glucose deprivation. Four hours after OGD, hydroxyl radical levels were determined using electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and the spin-trap compound, 5,5-dimethey-1-pyrroline-N-oxide (DMPO). There is a significant increase in hydroxyl radical generation that is attenuated by l-NAME (A). Slices were harvested and the amount of iron deposition determined (blue color). Representative images are shown (B). The intensity of blue color was increased by OGD, indicating increased iron deposition and this was attenuated by l-NAME (B and C). Values are presented as mean±S.E from 4 independent experiments using 24 pooled slices per experiment. *P<0.05 vs. No OGD, †P<0.05 vs. OGD no treatment.