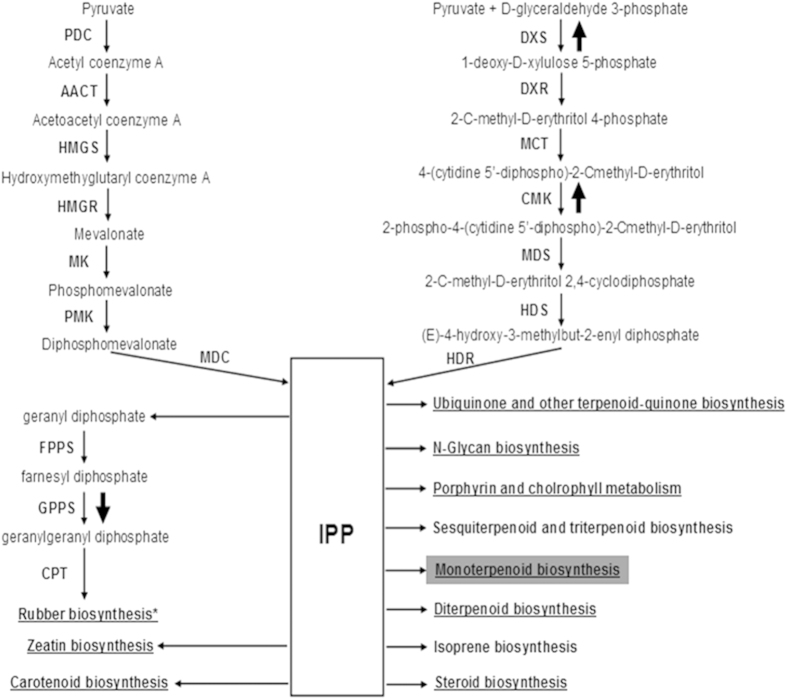
Figure 5. General pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis and the expression profiles of TPD-related genes.
IPP is a common intermediate for numerous isoprenoids and may be generated via the mevalonate (upper-left) or methylerythritol phosphate (upper-right) pathway in rubber trees. The IPP-requiring KEGG pathways that utilize IPP to synthesize different classes of isoprenoids are shown. The isoprenoid end-product KEGG pathways containing the assembled unigenes and DEGs identified in this study are underlined. The IPP-requiring KEGG pathway (monoterpenoid biosynthesis) in which the DEGs were enriched is highlighted in gray. PDC, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; AACT, acetyl coenzyme A acetyltransferase; HMGS, hydroxymethyglutaryl coenzyme A synthase; HMGR, hydroxymethyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; MK, mevalonate kinase; PMK, phosphomevalonate hosphomevalonate kinase; MDC, diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase; DXS, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase; DXR, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase; MCT, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase; MDS, 4-(cytidine 5′-diphospho)-2-Cmethyl-D-erythritol kinase; CMK, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; HDS, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate synthase; HDR, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; FPPS, farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase; GPPS, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase; CPT, cis-prenyltransferase. Compared with healthy trees, the upward and downward bold arrows indicate upregulated and downregulated of TPD-related genes, respectively, in TPD trees. *The locations of the two TPD-related genes HbREF and HbSRPP were not confirmed, and therefore they are not indicated in the RB pathway.